Masovian Voivodeship or Mazowieckie Province[4] or Mazowieckie Voivodeship[5] or Mazovian Voivodeship or Mazovian Province, etc.[6][7] (Polish: województwo mazowieckie, pronounced [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ mazɔˈvjɛt͡skʲɛ] ) is a voivodeship (province) in east-central Poland, containing Poland's capital Warsaw.
Masovian Voivodeship has an area of 35,579 square kilometres (13,737 sq mi) and had a 2019 population of 5,411,446, making it Poland's largest and most populous province.[1] Its principal cities are Warsaw (1.783 million) in the center of the Warsaw metropolitan area, Radom (212,230) to the south, Płock (119,709) to the west, Siedlce (77,990) to the east, and Ostrołęka (52,071) to the north. It borders six other provinces: Warmia-Mazury to the north, Podlaskie to the northeast, Lublin to the southeast, Holy Cross to the south, Łódź to the southwest, and Kujawy-Pomorze to the northwest.
The name of the province recalls the region's traditional name, Mazovia (in Polish Mazowsze, also spelled Masovia), with which it is roughly coterminous. However, the province's southern part, including Radom, historically belonged to Lesser Poland; while Łomża with environs, though historically part of Mazovia, is now part of Podlaskie Voivodeship.
Masovian Voivodeship is Poland's prime center of science, research, education, industry, and infrastructure.[8] It has Poland's lowest unemployment rate and is a very high-income province.[8] It is also popular with tourists due to the many historical monuments and its over 20% forested area of pine and oak.[9] The province's Kampinos National Park is a UNESCO biosphere reserve.

In the Early Middle Ages, the territory was inhabited by the Masovians, an old Polish tribe. It formed part of Poland since its establishment in the 10th century, with the then-regional capital Płock being the capital of Poland from 1079 to 1138. The Wzgórze Tumskie ("Cathedral Hill") in Płock with the Płock Castle and the Catholic Cathedral, seat of one of the oldest Polish dioceses, est. in 1075, which contains the sarcophagi of a number of Polish monarchs, is listed as a Historic Monument of Poland.[10] Later, Płock, Warsaw and Czersk were medieval ducal seats of the Piast dynasty.
In 1505, Radom hosted the session of the Sejm (Polish Parliament), which enacted the Nihil novi act, and in the 16th century, Warsaw hosted several sessions of the Sejm,[11] before King Sigismund III Vasa moved the Polish capital from Kraków to Warsaw in 1596.
Following the late-18th-century Partitions of Poland, the region witnessed several uprisings against foreign rule: the Kościuszko Uprising of 1794, the November Uprising of 1830–1831, and the January Uprising of 1863–1864.
In the interbellum, the region was part of reborn independent Poland. In 1920, the region was invaded by Soviet Russia, but Poland secured its freedom in the victorious Battle of Warsaw. The southern part of the current province was rapidly industrialized as part of the Central Industrial Region of Poland.
During World War II, it was occupied by Germany, with the occupiers committing their genocidal policies against Poles and Jews in the region, with expulsions, massacres of civilians and prisoners of war, including at Ciepielów, Śladów, Zakroczym, Ostrów Mazowiecka, Palmiry, Firlej, Ochota, and Wola. Germany operated numerous prisons, forced labour camps, the Treblinka extermination camp, in which some 700,000–900,000 people were murdered, and several prisoner-of-war camps for Polish, Italian, French, Soviet, and Romanian prisoners of war.[12]
Masovian Province was created on 1 January 1999, under the Polish local-government reforms adopted in 1998, out of the former provinces of Warsaw, Płock, Ciechanów, Ostrołęka, Siedlce, and Radom.
Masovian Voivodeship is divided into 42 counties, including five city counties and 37 land counties. These are subdivided into 314 gminas (municipalities), which include 85 urban gminas.

The voivodeship contains 10 cities and 78 towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures for 2019):[1]
Towns:

The Masovian voivodeship's government is headed by the province's voivode (governor) who is appointed by the Polish Prime Minister. The voivode is then assisted in performing his duties by the voivodeship's marshal, who is the appointed speaker for the voivodeship's executive and is elected by the sejmik (provincial assembly). The current voivode of Masovia is Konstanty Radziwiłł.
The Sejmik of Masovia consists of 51 members.

Protected areass include one National Park and nine Landscape parks. These are shown below.
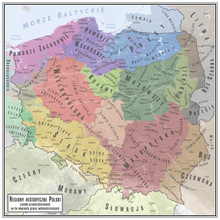
Masovia Voivodeship, 1526–1795 (Polish: Województwo Mazowieckie) was an administrative region of the Kingdom of Poland, and of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, from the 15th century until the partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (1795). Together with Płock and Rawa Voivodeships, it formed the province (prowincja) of Masovia.
Masovian Voivodeship was one of the voivodeships of Congress Poland. It was formed from the Warsaw Department and transformed into the Masovia Governorate.
,_Żmigród,_2015-12-05.jpg/440px-316B-002_(6),_Żmigród,_2015-12-05.jpg)
Three major international road routes pass through the voivodeship: Cork–Berlin–Poznań–Warszawa–Minsk–Moscow–Omsk (European route E30), Prague–Wrocław–Warsaw–Białystok–Helsinki (E67) and Pskov–Gdańsk–Warsaw–Kraków–Budapest (E77).
Currently, there are various stretches of highways in the area, with the A2 highway connecting the region, and therefore the capital city, with the rest of Europe. The highway passes directly through the voivodeship from west to east, connecting it with Belarus and Germany. However, the A2 is yet to be built east of Warsaw to connect Poland with Belarus. The S7 expressway runs through Poland from the north to the south passing through Warsaw, the S8 connects Warsaw with Białystok, in the neighboring north-eastern province, also forming part of the Via Baltica which heads on to Lithuania, and to Wrocław in the south-west, and the S17 being built to connect Warsaw with Lublin in the south-east and on to Ukraine.
The two main railway carriers operating in the region are the regional Koleje Mazowieckie and nationwide PKP Intercity. Three of ten busiest railway stations of Poland are located in the voivodeship: Warszawa Centralna, Warszawa Wschodnia, Warszawa Zachodnia.[20]
The main international airport in the region is Warsaw Frederic Chopin Airport.
Masovian Voivodeship is the wealthiest province in Poland. The gross domestic product (GDP) of the province was PLN 596 billion in 2021, accounting for 22.8% of the Polish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was around PLN123,000in the same year.[21]
The unemployment rate stood at 4.8% in 2017 and was higher than the national and the European average.[22]
.jpg/440px-Poland-00851_-_Castle_Square_(30848714790).jpg)
The top tourist destination of the voivodeship is the capital city of Warsaw with its Old Town and Royal Castle, a UNESCO World Heritage Site and Historic Monument of Poland.[23] Further Historic Monuments in Warsaw include the Royal Route with several palaces and parks, most notably the Łazienki Palace and Wilanów Palace, and the Warsaw Water Filters.
Other historic cities include Radom with its old center and parks, Pułtusk with the longest paved marketplace of Europe, and Płock, former medieval capital of Poland, with its Old Town and Wzgórze Tumskie ("Cathedral Hill") with the Płock Castle and the Płock Cathedral, which contains the sarcophagi of a number of Polish monarchs.
There are several medieval castles, including at Ciechanów, Czersk, Liw, Płock, and numerous palaces in the voivodeship, including at Otwock Wielki, Guzów, Radziejowice, Krubki-Górki, Sanniki, Korczew and multiple in Warsaw itself. Unique historic churches include the Temple of Mercy and Charity in Płock, the worldwide headquarters of the Mariavite Church, the Abbey Church in Czerwińsk nad Wisłą, one of the best preserved Romanesque fortified churches in Poland, and the Saints Roch and John the Baptist church in Brochów, a Gothic-Renaissance fortified church, place of baptism of Fryderyk Chopin. Otwock, Józefów and Warsaw are home to the local Świdermajer architectural style. There are also the Modlin Fortress and Warsaw Citadel.
The sole spa town of the voivodeship is Konstancin-Jeziorna.
There are museums dedicated to composer Fryderyk Chopin and chemist Marie Curie at their birthplaces in Żelazowa Wola and Warsaw, respectively. There is also a Fryderyk Chopin Museum in Warsaw. There is a museum dedicated to famous Renaissance poet Jan Kochanowski in Czarnolas. The Krasiński Palace in Opinogóra Górna hosts the Museum of Romanticism.
There are numerous World War II memorials, including memorials at the sites of Nazi massacres of Poles, including Palmiry, and Holocaust memorials, and museums at the sites of the former Nazi German Treblinka extermination camp, Pawiak Prison in Warsaw and Dulag 121 camp in Pruszków.

Football, handball, volleyball and basketball enjoy the largest following in the voivodeship. Successful clubs include Legia Warsaw and Polonia Warsaw in football and basketball, and Wisła Płock in handball.
Since the establishment of the province, several major international sports competitions were co-hosted by the province, including the 2002 World Weightlifting Championships, 2003 World Short Track Speed Skating Championships, 2009 UCI Track Cycling World Championships, EuroBasket 2009, UEFA Euro 2012, 2014 FIVB Volleyball Men's World Championship, 2017 Men's European Volleyball Championship, 2018 FIVB Volleyball Men's Club World Championship, 2019 UCI Track Cycling World Championships, 2023 World Men's Handball Championship.
Deepspot, the world's second deepest swimming pool, is located in Mszczonów.