
Медиана набора чисел — это значение, отделяющее верхнюю половину от нижней половины выборки данных , генеральной совокупности или распределения вероятностей . Для набора данных его можно рассматривать как «среднее» значение . Например, медианный доход может быть лучшим способом описания центра распределения доходов , поскольку увеличение крупнейших доходов само по себе не влияет на медиану. По этой причине медиана имеет центральное значение в надежной статистике .
Медиана конечного списка чисел — это «среднее» число, когда эти числа перечислены в порядке от наименьшего к наибольшему.
Если набор данных имеет нечетное количество наблюдений, выбирается среднее. Например, следующий список из семи чисел:
имеет медиану 6 , что является четвертым значением.
Если в наборе данных четное количество наблюдений, четкого среднего значения не существует, и медиана обычно определяется как среднее арифметическое двух средних значений. [1] [2] Например, этот набор данных из 8 чисел
имеет медианное значение 4,5 , т.е. (В более технических терминах это интерпретирует медиану как полностью урезанный средний диапазон ).
В общем, согласно этому соглашению, медиану можно определить следующим образом: Для набора данных элементов , упорядоченных от наименьшего к наибольшему,
Формально медианой популяции является любое значение, при котором по крайней мере половина населения меньше или равна предлагаемой медиане и по крайней мере половина больше или равна предлагаемой медиане. Как видно выше, медианы могут не быть уникальными. Если каждый набор содержит более половины населения, то часть населения в точности равна уникальной медиане.
Медиана четко определена для любых упорядоченных (одномерных) данных и не зависит от какой-либо метрики расстояния . Таким образом, медиану можно применять к школьным классам, которые имеют рейтинг, а не числовые значения (например, вычисление средней оценки, когда результаты тестов учащихся оцениваются от F до A), хотя результат может быть на полпути между классами, если количество классов четное. . (Для классов с нечетными числами один конкретный класс определяется как медиана.)
С другой стороны, геометрическая медиана определяется в любом количестве измерений . Родственная концепция, в которой результат вынужден соответствовать члену выборки, — это медоид .
Не существует общепринятого стандартного обозначения медианы, но некоторые авторы представляют медиану переменной x как med( x ), x͂ , [3] как µ 1/2 , [1] или как M . [3] [4] В любом из этих случаев использование тех или иных символов медианы должно быть явно определено при их введении.
Медиана является частным случаем других способов суммирования типичных значений, связанных со статистическим распределением : это 2-й квартиль , 5-й дециль и 50-й процентиль .
Медиану можно использовать в качестве меры местоположения , когда экстремальным значениям придается меньшее значение, обычно потому, что распределение искажено , экстремальные значения неизвестны или выбросы не заслуживают доверия, т. е. могут быть ошибками измерения/транскрипции.
Например, рассмотрим мультимножество
Медиана в данном случае равна 2, как и мода , и ее можно рассматривать как лучшее указание на центр , чем среднее арифметическое 4, которое больше, чем все значения, кроме одного. Однако широко цитируемая эмпирическая зависимость о том, что среднее значение смещается «дальше в хвост» распределения, чем медиана, в целом не соответствует действительности. В лучшем случае можно сказать, что эти две статистики не могут находиться «слишком далеко» друг от друга; см. § Средние и медианы, относящиеся к неравенству, ниже. [5]
Поскольку медиана основана на средних данных в наборе, для ее расчета не обязательно знать значение крайних результатов. Например, в психологическом тесте, исследующем время, необходимое для решения проблемы, если небольшому количеству людей вообще не удалось решить проблему за заданное время, все равно можно рассчитать медиану. [6]
Поскольку медиану легко понять и легко рассчитать, а также она является надежным приближением к среднему значению , медиана является популярной сводной статистикой в описательной статистике . В этом контексте существует несколько вариантов измерения изменчивости : диапазон , межквартильный диапазон , среднее абсолютное отклонение и медианное абсолютное отклонение .
В практических целях различные показатели местоположения и дисперсии часто сравниваются на основе того, насколько хорошо можно оценить соответствующие значения численности населения на основе выборки данных. Медиана, рассчитанная с использованием выборочной медианы, имеет в этом отношении хорошие свойства. Хотя обычно предполагается, что данное распределение населения не является оптимальным, его свойства всегда достаточно хорошие. Например, сравнение эффективности оценщиков -кандидатов показывает, что выборочное среднее является более статистически эффективным, когда — и только тогда — данные не загрязнены данными из распределений с тяжелым хвостом или из смесей распределений. [ нужна цитата ] Даже в этом случае эффективность медианы составляет 64% по сравнению со средним значением минимальной дисперсии (для больших нормальных выборок), то есть дисперсия медианы будет на ~ 50% больше, чем дисперсия среднего значения. [7] [8]
Для любого действительного распределения вероятностей с кумулятивной функцией распределения F медиана определяется как любое действительное число m , которое удовлетворяет неравенствам
Эквивалентная формулировка использует случайную величину X, распределенную согласно F :
Обратите внимание, что это определение не требует, чтобы X имело абсолютно непрерывное распределение (которое имеет функцию плотности вероятности f ), а также не требует дискретного распределения . В первом случае неравенства можно повысить до равенства: медиана удовлетворяет
Любое распределение вероятностей в множестве действительных чисел имеет по крайней мере одну медиану, но в патологических случаях медиан может быть более одной: если F постоянна 1/2 на интервале (так что там f = 0), то любое значение этого интервал является медианой.
Медианы некоторых типов распределений можно легко рассчитать по их параметрам; более того, они существуют даже для некоторых распределений, в которых отсутствует четко определенное среднее значение, таких как распределение Коши :
Средняя абсолютная ошибка действительной переменной c по отношению к случайной величине X равна
При условии, что распределение вероятностей X таково, что вышеуказанное ожидание существует, тогда m является медианой X тогда и только тогда, когда m является минимизатором средней абсолютной ошибки по отношению к X . [11] В частности, если m является выборочной медианой, то оно минимизирует среднее арифметическое абсолютных отклонений. [12] Однако обратите внимание, что в случаях, когда выборка содержит четное количество элементов, этот минимизатор не является уникальным.
В более общем смысле медиана определяется как минимум
как обсуждается ниже в разделе о многомерных медианах (в частности, пространственной медиане ).
Это основанное на оптимизации определение медианы полезно при статистическом анализе данных, например, при кластеризации k -медиан .
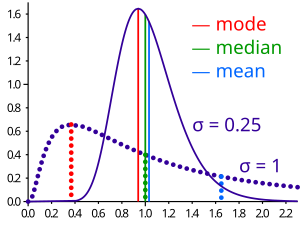
Если распределение имеет конечную дисперсию, то расстояние между медианой и средним значением ограничено одним стандартным отклонением .
Эта оценка была доказана Буком и Шером в 1979 году для дискретных выборок [13] и, в более общем плане, Пейджем и Мерти в 1982 году. [14] В комментарии к последующему доказательству О'Киннеида [15] Маллоуз в 1991 году представил компактное доказательство, дважды использующее неравенство Йенсена , [16] следующим образом. Использование |·| для абсолютного значения мы имеем
Первое и третье неравенства происходят из неравенства Йенсена, примененного к функции абсолютного значения и квадратичной функции, каждая из которых выпукла. Второе неравенство связано с тем, что медиана минимизирует функцию абсолютного отклонения .
Доказательство Маллоуза можно обобщить, чтобы получить многомерную версию неравенства [17], просто заменив абсолютное значение нормой :
где m — пространственная медиана , то есть минимизатор функции. Пространственная медиана уникальна, если размерность набора данных равна двум или более. [18] [19]
Альтернативное доказательство использует одностороннее неравенство Чебышева; оно проявляется в неравенстве параметров местоположения и масштаба . Эта формула также следует непосредственно из неравенства Кантелли . [20]
For the case of unimodal distributions, one can achieve a sharper bound on the distance between the median and the mean:
A similar relation holds between the median and the mode:
Jensen's inequality states that for any random variable X with a finite expectation E[X] and for any convex function f
This inequality generalizes to the median as well. We say a function f: R → R is a C function if, for any t,
is a closed interval (allowing the degenerate cases of a single point or an empty set). Every convex function is a C function, but the reverse does not hold. If f is a C function, then
If the medians are not unique, the statement holds for the corresponding suprema.[22]
Even though comparison-sorting n items requires Ω(n log n) operations, selection algorithms can compute the kth-smallest of n items with only Θ(n) operations. This includes the median, which is the n/2th order statistic (or for an even number of samples, the arithmetic mean of the two middle order statistics).[23]
Selection algorithms still have the downside of requiring Ω(n) memory, that is, they need to have the full sample (or a linear-sized portion of it) in memory. Because this, as well as the linear time requirement, can be prohibitive, several estimation procedures for the median have been developed. A simple one is the median of three rule, which estimates the median as the median of a three-element subsample; this is commonly used as a subroutine in the quicksort sorting algorithm, which uses an estimate of its input's median. A more robust estimator is Tukey's ninther, which is the median of three rule applied with limited recursion:[24] if A is the sample laid out as an array, and
then
The remedian is an estimator for the median that requires linear time but sub-linear memory, operating in a single pass over the sample.[25]
The distributions of both the sample mean and the sample median were determined by Laplace.[26] The distribution of the sample median from a population with a density function is asymptotically normal with mean and variance[27]
where is the median of and is the sample size:
A modern proof follows below. Laplace's result is now understood as a special case of the asymptotic distribution of arbitrary quantiles.
For normal samples, the density is , thus for large samples the variance of the median equals [7] (See also section #Efficiency below.)
We take the sample size to be an odd number and assume our variable continuous; the formula for the case of discrete variables is given below in § Empirical local density. The sample can be summarized as "below median", "at median", and "above median", which corresponds to a trinomial distribution with probabilities , and . For a continuous variable, the probability of multiple sample values being exactly equal to the median is 0, so one can calculate the density of at the point directly from the trinomial distribution:
Now we introduce the beta function. For integer arguments and , this can be expressed as . Also, recall that . Using these relationships and setting both and equal to allows the last expression to be written as
Hence the density function of the median is a symmetric beta distribution pushed forward by . Its mean, as we would expect, is 0.5 and its variance is . By the chain rule, the corresponding variance of the sample median is
The additional 2 is negligible in the limit.
In practice, the functions and above are often not known or assumed. However, they can be estimated from an observed frequency distribution. In this section, we give an example. Consider the following table, representing a sample of 3,800 (discrete-valued) observations:
Because the observations are discrete-valued, constructing the exact distribution of the median is not an immediate translation of the above expression for ; one may (and typically does) have multiple instances of the median in one's sample. So we must sum over all these possibilities:
Here, i is the number of points strictly less than the median and k the number strictly greater.
Using these preliminaries, it is possible to investigate the effect of sample size on the standard errors of the mean and median. The observed mean is 3.16, the observed raw median is 3 and the observed interpolated median is 3.174. The following table gives some comparison statistics.
The expected value of the median falls slightly as sample size increases while, as would be expected, the standard errors of both the median and the mean are proportionate to the inverse square root of the sample size. The asymptotic approximation errs on the side of caution by overestimating the standard error.
The value of —the asymptotic value of where is the population median—has been studied by several authors. The standard "delete one" jackknife method produces inconsistent results.[28] An alternative—the "delete k" method—where grows with the sample size has been shown to be asymptotically consistent.[29] This method may be computationally expensive for large data sets. A bootstrap estimate is known to be consistent,[30] but converges very slowly (order of ).[31] Other methods have been proposed but their behavior may differ between large and small samples.[32]
The efficiency of the sample median, measured as the ratio of the variance of the mean to the variance of the median, depends on the sample size and on the underlying population distribution. For a sample of size from the normal distribution, the efficiency for large N is
The efficiency tends to as tends to infinity.
In other words, the relative variance of the median will be , or 57% greater than the variance of the mean – the relative standard error of the median will be , or 25% greater than the standard error of the mean, (see also section #Sampling distribution above.).[33]
For univariate distributions that are symmetric about one median, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator is a robust and highly efficient estimator of the population median.[34]
If data is represented by a statistical model specifying a particular family of probability distributions, then estimates of the median can be obtained by fitting that family of probability distributions to the data and calculating the theoretical median of the fitted distribution. Pareto interpolation is an application of this when the population is assumed to have a Pareto distribution.
Previously, this article discussed the univariate median, when the sample or population had one-dimension. When the dimension is two or higher, there are multiple concepts that extend the definition of the univariate median; each such multivariate median agrees with the univariate median when the dimension is exactly one.[34][35][36][37]
The marginal median is defined for vectors defined with respect to a fixed set of coordinates. A marginal median is defined to be the vector whose components are univariate medians. The marginal median is easy to compute, and its properties were studied by Puri and Sen.[34][38]
The geometric median of a discrete set of sample points in a Euclidean space is the[a] point minimizing the sum of distances to the sample points.
In contrast to the marginal median, the geometric median is equivariant with respect to Euclidean similarity transformations such as translations and rotations.
If the marginal medians for all coordinate systems coincide, then their common location may be termed the "median in all directions".[40] This concept is relevant to voting theory on account of the median voter theorem. When it exists, the median in all directions coincides with the geometric median (at least for discrete distributions).
When dealing with a discrete variable, it is sometimes useful to regard the observed values as being midpoints of underlying continuous intervals. An example of this is a Likert scale, on which opinions or preferences are expressed on a scale with a set number of possible responses. If the scale consists of the positive integers, an observation of 3 might be regarded as representing the interval from 2.50 to 3.50. It is possible to estimate the median of the underlying variable. If, say, 22% of the observations are of value 2 or below and 55.0% are of 3 or below (so 33% have the value 3), then the median is 3 since the median is the smallest value of for which is greater than a half. But the interpolated median is somewhere between 2.50 and 3.50. First we add half of the interval width to the median to get the upper bound of the median interval. Then we subtract that proportion of the interval width which equals the proportion of the 33% which lies above the 50% mark. In other words, we split up the interval width pro rata to the numbers of observations. In this case, the 33% is split into 28% below the median and 5% above it so we subtract 5/33 of the interval width from the upper bound of 3.50 to give an interpolated median of 3.35. More formally, if the values are known, the interpolated median can be calculated from
Alternatively, if in an observed sample there are scores above the median category, scores in it and scores below it then the interpolated median is given by
For univariate distributions that are symmetric about one median, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator is a robust and highly efficient estimator of the population median; for non-symmetric distributions, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator is a robust and highly efficient estimator of the population pseudo-median, which is the median of a symmetrized distribution and which is close to the population median.[41] The Hodges–Lehmann estimator has been generalized to multivariate distributions.[42]
The Theil–Sen estimator is a method for robust linear regression based on finding medians of slopes.[43]
The median filter is an important tool of image processing, that can effectively remove any salt and pepper noise from grayscale images.
In cluster analysis, the k-medians clustering algorithm provides a way of defining clusters, in which the criterion of maximising the distance between cluster-means that is used in k-means clustering, is replaced by maximising the distance between cluster-medians.
This is a method of robust regression. The idea dates back to Wald in 1940 who suggested dividing a set of bivariate data into two halves depending on the value of the independent parameter : a left half with values less than the median and a right half with values greater than the median.[44] He suggested taking the means of the dependent and independent variables of the left and the right halves and estimating the slope of the line joining these two points. The line could then be adjusted to fit the majority of the points in the data set.
Nair and Shrivastava in 1942 suggested a similar idea but instead advocated dividing the sample into three equal parts before calculating the means of the subsamples.[45] Brown and Mood in 1951 proposed the idea of using the medians of two subsamples rather the means.[46] Tukey combined these ideas and recommended dividing the sample into three equal size subsamples and estimating the line based on the medians of the subsamples.[47]
Any mean-unbiased estimator minimizes the risk (expected loss) with respect to the squared-error loss function, as observed by Gauss. A median-unbiased estimator minimizes the risk with respect to the absolute-deviation loss function, as observed by Laplace. Other loss functions are used in statistical theory, particularly in robust statistics.
The theory of median-unbiased estimators was revived by George W. Brown in 1947:[48]
An estimate of a one-dimensional parameter θ will be said to be median-unbiased if, for fixed θ, the median of the distribution of the estimate is at the value θ; i.e., the estimate underestimates just as often as it overestimates. This requirement seems for most purposes to accomplish as much as the mean-unbiased requirement and has the additional property that it is invariant under one-to-one transformation.
— page 584
Further properties of median-unbiased estimators have been reported.[49][50][51][52] Median-unbiased estimators are invariant under one-to-one transformations.
There are methods of constructing median-unbiased estimators that are optimal (in a sense analogous to the minimum-variance property for mean-unbiased estimators). Such constructions exist for probability distributions having monotone likelihood-functions.[53][54] One such procedure is an analogue of the Rao–Blackwell procedure for mean-unbiased estimators: The procedure holds for a smaller class of probability distributions than does the Rao—Blackwell procedure but for a larger class of loss functions.[55]
Scientific researchers in the ancient near east appear not to have used summary statistics altogether, instead choosing values that offered maximal consistency with a broader theory that integrated a wide variety of phenomena.[56] Within the Mediterranean (and, later, European) scholarly community, statistics like the mean are fundamentally a medieval and early modern development. (The history of the median outside Europe and its predecessors remains relatively unstudied.)
The idea of the median appeared in the 6th century in the Talmud, in order to fairly analyze divergent appraisals.[57][58] However, the concept did not spread to the broader scientific community.
Instead, the closest ancestor of the modern median is the mid-range, invented by Al-Biruni[59]: 31 [60] Transmission of his work to later scholars is unclear. He applied his technique to assaying currency metals, but, after he published his work, most assayers still adopted the most unfavorable value from their results, lest they appear to cheat.[59]: 35–8 [61] However, increased navigation at sea during the Age of Discovery meant that ship's navigators increasingly had to attempt to determine latitude in unfavorable weather against hostile shores, leading to renewed interest in summary statistics. Whether rediscovered or independently invented, the mid-range is recommended to nautical navigators in Harriot's "Instructions for Raleigh's Voyage to Guiana, 1595".[59]: 45–8
The idea of the median may have first appeared in Edward Wright's 1599 book Certaine Errors in Navigation on a section about compass navigation.[62] Wright was reluctant to discard measured values, and may have felt that the median — incorporating a greater proportion of the dataset than the mid-range — was more likely to be correct. However, Wright did not give examples of his technique's use, making it hard to verify that he described the modern notion of median.[56][60][b] The median (in the context of probability) certainly appeared in the correspondence of Christiaan Huygens, but as an example of a statistic that was inappropriate for actuarial practice.[56]
The earliest recommendation of the median dates to 1757, when Roger Joseph Boscovich developed a regression method based on the L1 norm and therefore implicitly on the median.[56][63] In 1774, Laplace made this desire explicit: he suggested the median be used as the standard estimator of the value of a posterior PDF. The specific criterion was to minimize the expected magnitude of the error; where is the estimate and is the true value. To this end, Laplace determined the distributions of both the sample mean and the sample median in the early 1800s.[26][64] However, a decade later, Gauss and Legendre developed the least squares method, which minimizes to obtain the mean. Within the context of regression, Gauss and Legendre's innovation offers vastly easier computation. Consequently, Laplaces' proposal was generally rejected until the rise of computing devices 150 years later (and is still a relatively uncommon algorithm).[65]
Antoine Augustin Cournot in 1843 was the first[66] to use the term median (valeur médiane) for the value that divides a probability distribution into two equal halves. Gustav Theodor Fechner used the median (Centralwerth) in sociological and psychological phenomena.[67] It had earlier been used only in astronomy and related fields. Gustav Fechner popularized the median into the formal analysis of data, although it had been used previously by Laplace,[67] and the median appeared in a textbook by F. Y. Edgeworth.[68] Francis Galton used the English term median in 1881,[69][70] having earlier used the terms middle-most value in 1869, and the medium in 1880.[71][72]
Statisticians encouraged the use of medians intensely throughout the 19th century for its intuitive clarity. However, the notion of median does not lend itself to the theory of higher moments as well as the arithmetic mean does, and is much harder to compute. As a result, the median was steadily supplanted as a notion of generic average by the arithmetic mean during the 20th century.[56][60]
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of January 2024 (link)This article incorporates material from Median of a distribution on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.