ITV , официально известный как Channel 3 , — британская общественная телевизионная сеть бесплатного вещания . На большей части территории Великобритании он имеет торговую марку ITV1, за исключением центральной и северной Шотландии, где он имеет торговую марку STV . Оно было создано в 1955 году как Независимое телевидение, чтобы обеспечить конкуренцию и устранить то, что до сих пор было монополией телевидения BBC (основанного в 1936 году). [1] ITV — старейшая коммерческая сеть в Великобритании. С момента принятия Закона о вещании 1990 года он был официально известен как Канал 3, чтобы отличать его от других аналоговых каналов того времени: BBC1 , BBC2 и Channel 4 .
ITV на протяжении четырех десятилетий представляла собой сеть отдельных компаний, которые предоставляли услуги регионального телевидения, а также делились программами между собой для показа по всей сети. Каждая франшиза изначально принадлежала отдельной компании. После нескольких слияний пятнадцать региональных франшиз теперь принадлежат двум компаниям: ITV plc , которая управляет каналом ITV1 и каналом UTV , который теперь называется ITV1, и STV Group , которая управляет каналом СТВ .
Сеть ITV является отдельным предприятием от ITV plc, компании, возникшей в результате слияния Granada plc и Carlton Communications в 2004 году. ITV plc владеет лицензиями на вещание Channel 3 для всех регионов, за исключением центральной и северной Шотландии, которыми владеет STV. Группа.
Сегодня ITV plc просто централизованно заказывает расписание сети; программы производятся собственной дочерней компанией ITV Studios и независимыми продюсерскими компаниями. Региональные программы остаются в новостях и некоторых сериалах о текущих событиях.
В Северной Ирландии компания ITV plc использовала торговую марку UTV в качестве названия канала, пока канал ITV не был переименован в ITV1; Однако он по-прежнему используется для показанных здесь местных программ. Это имя использовал бывший владелец UTV Media (теперь известный как News Broadcasting ). ITV plc купила UTV в 2016 году.
Хотя история сети ITV восходит к 1955 году, с течением времени многие региональные франчайзи изменились. Некоторые из наиболее важных имен в прошлом сети, в частности Thames , ABC и ATV , не имеют никакого отношения к современной сети.


Истоки ITV лежат в принятии Закона о телевидении 1954 года , призванного разрушить монополию на телевидение, принадлежащую телевизионной службе BBC . [1] Закон создал Независимое управление телевидения (ITA, затем IBA после Закона о звуковом вещании) для жесткого регулирования отрасли и предоставления франшиз. Первые шесть франшиз были предоставлены в 1954 году для Лондона, Мидлендса и севера Англии, с отдельными франшизами для будних и выходных дней. [1] Первой запущенной службой ITV была лондонская Associated-Rediffusion 22 сентября 1955 года, [2] услуги Midlands и North были запущены в феврале 1956 года и мае 1956 года соответственно. После этих запусков ITA предоставила больше франшиз, пока вся страна не была покрыта четырнадцатью региональными станциями, все из которых были запущены к 1962 году.
Сеть несколько раз модифицировалась в ходе проверок франшизы, которые проводились в 1963, [3] 1967, [4] 1974, [5] 1980 [6] [7] и 1991, [8] во время которых менялись регионы вещания и операторы сервиса заменены. Только один оператор связи был объявлен банкротом, WWN в 1963 году, [9] при этом все остальные операторы покинули сеть в результате проверки франшизы. Отдельные франшизы выходного дня были удалены в 1968 году (за исключением Лондона) [3], и с годами было добавлено больше услуг; в их число входила программа национальных завтраков с 1983 года, работающая с 6:00 до 9:25 утра, а также служба телетекста. [6] Закон о вещании 1990 года изменил природу ITV; тогдашний регулятор IBA был заменен регулятором с легким касанием ITC ; компании получили возможность приобретать другие региональные компании ITV [10], и франшизы теперь предоставлялись на основе аукциона с самой высокой ставкой, с небольшими гарантиями. [8] В этой подвергшейся резкой критике части обзора были заменены четыре оператора, и операторы столкнулись с различными ежегодными платежами в Казначейство : Центральное телевидение, например, заплатило всего 2000 фунтов стерлингов — несмотря на то, что владело прибыльным и большим регионом — потому что этому не встречали сопротивления, в то время как Йоркширское телевидение заплатило 37,7 миллиона фунтов стерлингов за регион такого же размера и статуса из-за жесткой конкуренции. [8] [11]
После изменений 1993 года ITV как сеть начала объединяться с несколькими компаниями, делая это, чтобы сэкономить деньги за счет прекращения дублирования услуг, существовавших, когда все они были отдельными компаниями. К 2004 году сеть ITV принадлежала пяти компаниям, две из которых, Carlton и Granada, стали крупными игроками, владея всеми франшизами в Англии, Уэльсе, на шотландских границах и на острове Мэн. [12] [13] [14] В том же году они объединились и образовали ITV plc. [12] [13] [14] единственными последующими приобретениями стали поглощение Channel Television , франшизы Нормандских островов, в 2011 году; [15] и UTV, франшиза Северной Ирландии, в 2015 году.
Сеть ITV принадлежит и управляется не одной компанией, а несколькими лицензиатами, которые предоставляют региональные услуги, а также транслируют программы по сети. С 2016 года пятнадцать лицензий принадлежат двум компаниям, большая часть которых принадлежит ITV Broadcasting Limited, входящей в состав ITV plc.
Сеть регулируется регулятором СМИ Ofcom , который отвечает за выдачу лицензий на вещание. Последний крупный пересмотр франшиз Channel 3 состоялся в 1991 году, при этом лицензии всех операторов были продлены в период с 1999 по 2002 год, а затем снова с 2014 года без дальнейшего конкурса. Хотя это был самый длительный период, когда сеть ITV обходилась без серьезной проверки держателей лицензий, Ofcom объявил (после консультации), что с 1 января 2014 года разделит лицензии Уэльса и Запада , создав национальную лицензию для Уэльса и присоединившись к ней. недавно отделенный Западный регион к Westcountry Television , чтобы сформировать новую лицензию для расширенного региона Юго-Запад Англии.
Все компании, имеющие лицензию, входили в некоммерческую организацию ITV Network Limited, которая заказывала и планировала сетевые программы, соблюдение которых ранее контролировалось ITV plc и Channel Television . Однако из-за объединения нескольких из этих компаний с момента создания ITV Network Limited (и учитывая, что Channel Television теперь принадлежит ITV plc), она была заменена системой филиалов. [16] По одобрению Ofcom, это приводит к вводу в эксплуатацию ITV plc и финансированию расписания сети, при этом STV и UTV платят плату за его трансляцию. [16] Все лицензиаты имеют право отказаться от сетевых программ (за исключением национальных бюллетеней новостей), но, в отличие от предыдущей системы, за это не будет возмещена плата. Поэтому многие не отказываются от участия из-за давления со стороны материнской компании или из-за ограниченности ресурсов. [16] До введения партнерской системы телеканал STV часто (а иногда и спорно) отказывался от участия в нескольких популярных сетевых программах – например, в оригинальном выпуске первой серии « Аббатства Даунтон» , – ссылаясь на необходимость предоставлять больше шотландского контента для своих каналов. зрители. [17]
Как общественная телекомпания, сеть ITV обязана транслировать программы общественного значения, включая новости, текущие события, детские и религиозные программы, а также трансляции партийных выборов от имени основных политических партий и политических событий, таких как бюджет. Сеть также должна создавать доступные выходные данные, содержащие субтитры, подписи и аудиоописания. В обмен на эти программы сеть ITV доступна на всех платформах бесплатного вещания и ее можно найти в верхней части электронного гида передач всех провайдеров.
С момента запуска платформы в 1998 году все лицензиаты ITV получили в подарок возможности на платформе цифрового наземного телевидения . В настоящее время компании могут транслировать дополнительные каналы, и все они предпочитают транслировать принадлежащие ITV plc каналы ITV2 , ITV3 , ITV4 и ITVBe в своем регионе. UTV и STV (ранее Scottish Television и Grampian Television ) ранее транслировали свои собственные услуги — UTV2 в Северной Ирландии и S2 в центральной и северной Шотландии — до 2002 года, когда они переняли каналы ITV plc. Несмотря на это, СТВ получил лицензию на вещание того, что впоследствии стало каналом СТВ2 в 2013 году, однако это просуществовало недолго, и канал закрылся в 2018 году. Все вещательные компании используют мультиплекс Digital 3&4 , используемый совместно с Channel 4 . CITV запущен в марте 2006 г. (закрыт в сентябре 2023 г.). ITV Encore запущен в июне 2014 года (закрыт в мае 2018 года), а ITVBe запущен в октябре 2014 года. Кассовые сборы ITV запущены в феврале 2017 года (закрыты в январе 2020 года).
13 сентября 2022 года [18] ITV подтвердило, что в понедельник, 19 сентября, в день государственных похорон Ее Величества Королевы Елизаветы II , все расписания программ на цифровых каналах ITV будут отменены, а основное освещение новостей ITV будет отменено. транслируется в прямом эфире и непрерывно на всех каналах. [19] [18] Это был первый раз, когда ITV решила сделать это: компания сохраняла расписания своих цифровых каналов в основном такими, как рекламировалось в преддверии похорон (с некоторыми поправками в отношении отмененных спортивных мероприятий на ITV4) и всем остальным. королевское освещение на их основном канале. [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24]

ITV plc владеет тринадцатью из пятнадцати франшиз и вещает на Англию, Уэльс, южную Шотландию, остров Мэн, Нормандские острова и Северную Ирландию через свою дочернюю компанию ITV Broadcasting Limited. [15] Компания также владеет лицензией на телевидение для завтраков , [25] которое по состоянию на январь 2020 года транслируется по сети с 6:00 до 10:00 каждое утро с использованием имен Good Morning Britain (ранее Daybreak ) и Lorraine . Компания вещает централизованную услугу под брендом ITV1 . В Северной Ирландии ITV использовала торговую марку UTV в качестве названия канала до апреля 2020 года.
Группа также владеет ITV Studios , продюсерским подразделением компании, образованным в результате объединения всех производственных отделов региональных лицензий, которыми они владеют. Компания производит большую часть сетевых программ ITV (около 47%, но ранее, согласно некоторым отчетам, достигала 66% [26] ), а остальная часть поступает в основном от независимых поставщиков (согласно Закону о вещании 1990 года, не менее 25% общего объема продукции ITV должна приходиться на независимые компании). [27] ITV plc надеется увеличить количество собственных программ до максимально возможного уровня в 75%.
Группа сократила количество предлагаемых региональных новостных программ с 17 в 2007 году до 9 к 2009 году, в результате чего несколько регионов были объединены в одну программу, включая регионы Бордер и Тайн-Тис , регионы Весткантри и Запад , а также были удалены субрегиональные программы. при этом некоторые регионы представлены только заранее записанными сегментами. [28] Субрегионы были восстановлены в 2013 году.
STV Group plc владеет двумя франшизами, охватывающими центральную и северную Шотландию, через дочерние компании STV Central и STV North, транслирующие центральную службу под брендом STV .
В конце 2000-х - начале 2010-х годов у компании было несколько споров с ITV plc по поводу сетевых программ. STV стремилось транслировать больше шотландских программ в часы пик и поэтому в июле 2009 года исключило из своего расписания несколько ключевых программ ITV plc, включая «Билл» , «Убийства в Мидсомере» и «Льюис» . [29] Несмотря на объяснение STV о расходах, ITV plc была возмущена этим решением, поскольку недавнее изменение расписания сделало «Билл» центральным элементом их программ и транслировало программы также на ITV3 , чтобы гарантировать, что шотландские зрители смогут увидеть программы. 23 сентября сообщалось, что ITV plc подала иск против STV на 20 миллионов фунтов стерлингов, поскольку ITV посчитала, что прекращение шоу представляет собой нарушение сетевых соглашений; [30] Впоследствии STV подала встречный иск на ITV plc на 35 миллионов фунтов стерлингов.
Спор завершился в 2011 году, когда STV согласилась выплатить ITV plc 18 миллионов фунтов стерлингов. Подписание нового соглашения о присоединении привело к тому, что СТВ платит фиксированную плату за все сетевые программы, поэтому отказ от каких-либо программ маловероятен из-за больших затрат. [31]

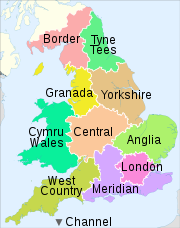
Существует пятнадцать региональных лицензий, охватывающих четырнадцать регионов (для региона Лондона существуют отдельные лицензии в будние и выходные дни) и одна национальная лицензия на обслуживание завтраков. Все перечисленные здесь лицензии были продлены до конца 2024 года. До ноября 2008 года лицензии в Англии и Уэльсе принадлежали отдельным региональным компаниям, принадлежащим ITV plc. [32]
Назначение на предоставление национальных новостей для Channel 3 также подлежит одобрению Ofcom. Это назначение осуществляется ITN с момента создания канала, а также утверждено до конца 2024 года. [33]

За более чем 60 лет работы ITV его отечественные программы стали одними из самых запоминающихся, а также чрезвычайно успешными. До 1990-х годов почти весь контент канала производился пятнадцатью лицензиатами франшизы: региональными компаниями.
Однако после принятия Закона о радиовещании 1990 года, устанавливающего 25%-ную квоту на запуск независимого производства, [27] количество программ независимых продюсерских компаний, не подключенных к традиционной сети ITV, быстро возросло. Яркие примеры включают Talkback Thames (половина которой, Thames Television , сама была бывшим франчайзи ITV), продюсеры The Bill и сопродюсеры The X Factor , а также 2waytraffic , продюсеры Who Wants to Be a Millionaire? .
С конца 1990-х годов давняя приверженность ITV к активным текущим событиям и документальным программам начала уменьшаться с прекращением таких постановок, как « Мир в действии » ( Granada Television ), «На этой неделе» ( Rediffusion London / Thames Television ), «Первый вторник» ( Yorkshire Television). ), Network First , Survival ( Anglia Television ) и Weekend World ( LWT ) и их замена популистскими шоу, такими как Tonight . Новости в Ten также были закрыты в 1999 году, но были восстановлены в 2001 году. В декабре 2009 года в эфир вышел последний выпуск многолетней художественной программы ITV « Шоу Южного берега» .
В расписании ITV в прайм-тайм преобладают мыльные оперы, такие как флагманские сериалы «Улица Коронации» и «Эммердейл» . В начале 21 века Независимое телевидение подверглось критике за включение в расписание большого количества программ «реалити-шоу», таких как « Celebrity Fit Club» , «Celebrity Wrestling» и «Celebrity Love Island» . В свою защиту ITV продолжает демонстрировать свои сильные стороны в области освещения спортивных событий и драматических постановок, а также продолжает планировать национальные новости в прайм-тайм.
Программы телевидения «Завтрак» транслировались на ITV во время завтрака с 1 февраля 1983 года. Первоначально ими управлял независимый подрядчик — TV-am , а затем GMTV — до тех пор, пока в ноябре 2009 года GMTV Limited не стала дочерней компанией ITV plc .
Исторически сложилось так, что ITV транслировал программы завтрака с 6 утра до 9:25 утра, но ITV продлил это время до 10 утра по будням 6 января 2020 года. [37] и теперь транслирует две программы завтрака по будням - «Доброе утро, Британия» и « Лотарингия» . «Доброе утро, Британия» держит зрителей в курсе всех последних новостей, спорта, телепередач и погоды, в то время как Лоррейн преимущественно фокусируется на интервью со знаменитостями, рецептах, моде и шоу-бизнесе. До сентября 2023 года служба будет показывать одновременную трансляцию канала citv, но после закрытия службы показывает смесь повторяющихся программ, в то время как служба citv, которая все еще существует, транслируется во время завтрака на канале ITV 2. ITV 3 и ITV 4, и это будет с 7 утра. показать другие повторы, некоторые из которых предоставляют услугу языка жестов в рамках трансляции в рамках квоты и лицензионных требований.
Сильный дневной состав ITV, которому помогают такие программы, как «Это утро» , «Свободные женщины» , «Реальная сделка Дикинсона» , а также игровые шоу «Переломный момент» и «Погоня», очень популярны, достигая наибольшей доли аудитории в дневное время. [38]
In recent years the network has tried to use formats that ITV Studios own outright (whether they have originated in the UK with their Lifted Entertainment[39] company or have come from production companies they own abroad), though some popular programme formats like The Masked Singer have still been acquired from other companies abroad. Currently ITV are behind the formats for Dancing on Ice, The Voice UK (the format originally coming from their Dutch production company) and I'm a Celebrity...Get Me Out of Here!, while forthcoming music game show Walk The Line has been co-developed by Simon Cowell's Syco Entertainment and ITV.[40][41][42][43]
Since the network started, Independent Television News Limited (ITN) has held the contract to produce news for the ITV network, with 30-minute national news bulletins currently broadcast at 1:30 pm, and 10:00 pm, and an hour-long bulletin at 6.30pm. These bulletins were broadcast under the ITN brand from 1955 until 1999, when a new network identity reinforced the ITV brand, resulting in the new bulletins being broadcast under the ITV News brand.[44][45]
ITN has long been respected in the news industry as a source of reliable information and news, and as a result the service has won many awards for their programmes, the latest being in May 2011 when News at Ten was named best news programme by the Royal Television Society and BAFTA.
The ITV National Weather forecast was first broadcast in 1989, using data supplied by the Met Office, and was presented by a number of weather forecasters. The forecasts are sponsored with the sponsor's message appearing before and after the forecast. The forecasts are made immediately after the main national news bulletins.
Prior to the creation of the national forecast, each regional company provided its own regional forecast. The regional forecasts today are incorporated into the main regional news bulletins, and in the summer months, includes a pollen count.
Currently only new episodes of long-form news and current affairs programmes like Exposure,[46] Peston[47] and On Assignment[48] are being scheduled after News at Ten, with the latter title currently only appearing on a month-by-month basis. The channel broadcasts a partnership teleshopping service for a couple of hours after midnight, the time between the news and the shopping is usually kept for re-runs, with ITV repeating its primetime entertainment shows or sports programming from ITV4.[49][50][51][52]
ITV continues with its regularly scheduled programming after the shop service finishes at around 3am with showbiz news bulletin FYI Extra[53] and repeats, many of which have on-screen BSL signing for the deaf community.[54] Replacing the information based ITV Nightscreen slot in 2021 was Unwind With ITV,[55] programming produced in association with the Campaign Against Living Miserably. At around 4am each night this mindfulness programme shows calming shots of natural landscapes and relaxing animations for around an hour,[56][57] with versions of the footage also seen on ITV2, ITV3 and ITV4.itv 2, 3 and 4 continue programmes till around 2.30 sometimes using the aforementioned unwind sequences to fill small pieces of time before this. TELESHOPPING on itv be starts at 1am and continues till 7am. There are some occasions when other coverage means this cycle of programmes get misplaced, for example a live event overnight or over Christmas the non sale of slots to TELESHOPPING meaning more repeats, films and long unwind sequences are used instead.Overnight Stv broadcasts an overnight news and information service mixing reports from Stv news and other information both instead of itvs shopping slot and also during the unwind slot. Due to Stv optouts this service can start later than or earlier than itvs shopping service. Stv did used to also the unwind slot but was phased out and replaced with the aforementioned news and information service instead. This overnight programme service is very different to what used to be shown on the network after 24 hour broadcasting this included new entertainment, imports, sports and other information programmes and in some regions a job finder service, however due to the small audience this was phased out and replaced by the service previously described. Before 24 hour tv the services simply closed down and restarted the following morning with breakfast tv and before that other scheduled programmes.
The regional ITV companies are required to provide local news as part of their franchise agreement together with local weather forecasts, with the main local bulletin at 6pm and regional bulletins located after each national news programme. In addition to this, traditionally ITV companies would provide other regional programming based on current affairs, entertainment or drama. However, apart from a monthly political programme, most non-news regional programming in the English regions was dropped by ITV plc in 2009, although it continues in Wales and the Channel Islands, as well as on STV and UTV and ITV Border in Scotland from 2014 to cover mainly Scottish politics whilst ITV Border in England broadcast network programming .[58] On 14 January 2013, ITV plc regional news programmes titles were discontinued in favour of more generic branding under the ITV News title with the region listed as the subheading. However some "heritage" brand names were retained including Calendar, Granada Reports and Lookaround. On 28 June 2014, ITV News Cymru Wales returned to its historic name of Wales at Six.

The network broadcasts children's programming under the CITV (Children's ITV) strand. Children's programming was originally provided during weekday afternoons and weekend mornings, however following the launch of the CITV channel in 2006, all children's programming, with the exception of the weekend ITV Breakfast slot, were relocated from the ITV line-up to the CITV channel in 2007, a move which was challenged by Ofcom in April 2007. In 2023, ITV announced that CITV would cease broadcasting as a linear channel, and would be replaced by ITVX Kids, which launched in July 2023.[69] The CITV channel closed on 1 September 2023, with a dedicated CITV programming block now broadcasting on ITV2 every morning, from 2 September 2023.
Schools programming on the network began in 1957 in some regions and expanded as more regions began broadcasting. It was a contractual obligation for some ITV companies to broadcast schools programming, and this was initially broadcast as part of the normal scheduling. The programmes were moved into a segment for broadcast during the day in the 1960s, under the banner Independent Television for Schools and Colleges and from 1987 were broadcast on Channel 4 in the ITV Schools on Channel 4 segment. In 1993, this segment became Channel 4 Schools and later in 2000 4Learning. These strands of programming consisted of schools programming from all the ITV companies or from independent sources. The schools strand itself is now defunct, with no particular branding segment used.
ITV was originally very reliant on broadcasting American series, with westerns such as Gunsmoke and Rawhide in particular being considerable successes for the network during its earlier years. Action drama The Fugitive and sci-fi anthology The Twilight Zone were also broadcast by various regions in the early 1960s, with Batman and I Dream of Jeannie shown later on in the decade. Due to the varying schedules of many ITV regions, acquired content was not broadcast by some franchises.
By the 1970s, most ITV regions were airing the likes of Hawaii Five-O, Happy Days, and The Brady Bunch. 1972 also saw the beginning of ITV's daytime programmes at lunchtime, a slot that would become associated with the many Australian soap operas that were broadcast in the newly expanded schedule, including The Sullivans and The Young Doctors. By the 1980s, more were added to the schedule, such as Sons and Daughters and A Country Practice.
In primetime by the 1980s, ITV was broadcasting the likes of Hill Street Blues (which ITV began showing just one week after its debut on NBC in the United States) and L.A. Law. It was also early in the decade when Australian evening soap opera Prisoner: Cell Block H was bought by ITV, and was broadcast after News at Ten.
By 1982, Channel 4 had launched, and despite originally being related to ITV, it competed against its parent network to screen popular American programmes such as St. Elsewhere and Cheers, although the latter did receive a single ITV broadcast as part of a night showcasing Channel 4 programmes. Both Hill Street Blues and L.A. Law had moved from ITV to Channel 4 by the end of their runs.
A heavy emphasis on action, fantasy and science fiction series was also placed by ITV during this 1980s, with The A-Team, Buck Rogers in the 25th Century, and Airwolf being broadcast by the network, as well as the likes of Baywatch and SeaQuest DSV by the 1990s. ITV also picked up a glut of older-skewing CBS dramas through that period, including Murder, She Wrote and Dr. Quinn, Medicine Woman.
In February 1989, in tandem with the network launching its national weather forecast, and as part of a new early evening lineup which involved the shortening of Children's ITV, Australian soap Home and Away was acquired by ITV, particularly to compete with the success of rival Australian soap opera Neighbours on BBC One. ITV also broadcast Beverly Hills, 90210 beginning in early 1991, in the same Saturday teatime slot that Baywatch had occupied, although some episodes were broadcast in later time slots. It moved to Sky One beginning with the third season.
ITV reshuffled its daytime schedules in the Autumn of 1993, and just a few months prior, Central began broadcasting the New Zealand soap opera Shortland Street. The revamp saw more ITV companies pick it up, with Scottish Television the only region to reject the series outright. Central also broadcast the Australian soap opera Echo Point around the same time, although no other franchises picked it up. ITV also aired a considerable amount of syndicated unscripted US programmes in daytime during the 90s, such as Judge Judy and The Jerry Springer Show.
By 1996, ITV had been quiet with US series in primetime, particularly as Channel 4 and Sky One increased the competition for securing the most popular US dramas and sitcoms. However, that summer, ITV debuted the primetime soap Savannah, in a 9pm Friday slot. It was a considerable success for ITV's standards, and it became the highest rated new American series of that year. Despite this success, ITV moved the show for its second season, no longer networking the series and moving to late night slots.
ITV tried again at broadcasting an American drama series in September 1997, with the ABC legal drama The Practice, which ran in the same slot that Savannah had the year prior. It saw nowhere near the same levels of success, and was dropped by the network after just three episodes. It later resurfaced in late night before moving to BBC One in 2000.
ITV attempted launching a Monday night block for American sitcoms in the post-News at Ten slot in the autumn of 1998, with Veronica's Closet (which ITV beat Channel 4 for the rights to) followed by Dharma & Greg.[70] After this failed to catch much steam, ITV all but pulled out from showing American programmes on the main network by the end of the decade, and it would prove to be the final time ITV aired US comedy on the main network.
ITV made attempts during the mid 2000s to poach proven popular US shows such as the mystery comedy-drama Desperate Housewives and medical drama House from Channel 4 and Five, respectively, but both shows ended up remaining on their incumbent rights holders.[71][72] ITV were reportedly also interested in 2004 about acquiring the Friends spin-off Joey but later denied such interest, and in 2007 were close to picking up Neighbours after the BBC declined to continue broadcasting it, although Five eventually won the rights to both programmes.[73][74][75]
ITV returned to US programming in 2006, acquiring Six Degrees.[76] Initially it had been planned to air in a primetime slot in 2007, but ended up being shown in late nights in 2008. This could be due to the show being cancelled after its first season by original network ABC due to low ratings, despite high expectations and its slot following top-10 hit Grey's Anatomy. It was also around this time that Supernatural and Dexter, which ITV2 & ITV4 aired respectively, were given late night repeats on ITV1.[77][78]
The following year, ITV acquired another US programme, fellow ABC series Pushing Daisies. It debuted in 2008 in a Saturday evening slot and initially did well garnering 5.7 million viewers, although there were fan complaints when ITV chose to skip broadcasting the second episode, blaming football coverage, eventually releasing it on their website.[79][80] The last attempt so far by ITV to broadcast acquired output in primetime was the TV adaption of Lethal Weapon in 2017, where it remained for all three seasons.
The Public Teletext Licence[81] allows the holder to broadcast a text-based information service around the clock on Channel 3 (as well as Channel 4 and S4C) frequencies. Teletext on ITV was provided by ORACLE from 1974 until 1993 and from 1993 to 2010 by Teletext Ltd., whose news, sport and TV listings pages rivalled the BBC's offering, Ceefax on terrestrial and BBC Red Button on digital. Teletext Ltd. also provided digital teletext for the Channel 3 services, as well as the text output for both Channel 4 and S4C under the same licence and Channel 5. However, the licence was revoked by Ofcom on 29 January 2010 for failing to provide news and local non-news information on ITV and there is currently no teletext licence holder for ITV.[82]
ITV (as UTV) is widely available in Ireland, where it is received directly in areas bordering Northern Ireland, or in coastal areas from Wales (as ITV Cymru Wales). Until 2015, it was also carried on cable, when it was replaced by UTV Ireland, which was itself replaced by be3, now Virgin Media Three. ITV programming is also available to Irish viewers on Virgin Media One (including soap operas Emmerdale and Coronation Street). ITV is also available on cable and IPTV in Switzerland and Liechtenstein. Since 27 March 2013, it has been offered by the British Forces Broadcasting Service (BFBS) to members of HM Forces and their families around the world, replacing the BFBS3 TV channel, which already carried a selection of ITV programmes.[83]
Since the launch of ITV, there have been concerns from politicians and the press that ITV faced a conflict concerning programme audiences and advertisers. As advertisers are reluctant to buy advertising space around low viewing programmes, there is a pressure on ITV to broadcast more popular programmes in peak times. This became more profound in the early 21st century, following a relaxation in regulation and significantly more competition in the advertising market following the huge increase in commercial channels. In the 2000s, programmes from the reality television genre including the celebrity and talent show subgenres became a dominant presence on the channel. This led to accusations of ITV 'dumbing down' their programmes and appealing to the 'lowest common denominator', accusations that are at odds with the network's status as a public service broadcaster.[84][85] ITV was/is also heavily criticised for scaling back its regional programmes, including regional news.
There has never been an identity for ITV as a whole that was adopted uniformly by all broadcasters within the ITV network. Before 1989, each regional company used its own name for identification and the name "ITV" was rarely seen on screen, except for some sub-brands such as ITV Schools or ITV Sport. In September 1989, a national ITV corporate identity was established, which saw regional brands combined with the national ITV brand, although the balance between regional and national brands varied from company to company, and some companies never used the ITV brand at all. It was not until October 2002 that national ITV-branded continuity was adopted across all the regions in England (see ITV1), although regional continuity before local programmes continued until November 2006.