Испанские и португальские евреи , также называемые западными сефардами , иберийскими евреями или евреями полуострова , представляют собой особую подгруппу сефардских евреев , которые в основном происходят от евреев, живших как новые христиане на Пиренейском полуострове в течение нескольких столетий после насильственного изгнания необращенные евреи из Испании в 1492 году и из Португалии в 1497 году . Поэтому их следует отличать как от потомков изгнанных в 1492 году, так и от современных еврейских общин Испании и Португалии.
Основные современные общины испанских и португальских евреев существуют в Нидерландах, Великобритании, США и Канаде, а несколько других еврейских общин в Америке имеют испанские и португальские еврейские корни, хотя они больше не следуют отличительным обычаям Испанские и португальские евреи.
Хотя изгнание необращенных евреев из Испании и Португалии в 1492 и 1497 годах было отдельными событиями от испанской и португальской инквизиций (которые были созданы более десяти лет назад, в 1478 году), в конечном итоге они были связаны, поскольку инквизиция в конечном итоге также привела к бегству из Иберия многих потомков евреев, принявших католицизм в последующих поколениях.
Несмотря на то, что первоначальные указы об изгнании не распространялись на новохристианских новообращенных еврейского происхождения — поскольку они теперь были законными христианами — дискриминационные практики, которые, тем не менее, применяла к ним инквизиция и которые часто были смертельными [ нужна цитата ] , оказывали огромное давление на многих христиан еврейского происхождения также эмигрировать из Испании и Португалии в ближайшие поколения после изгнания их необращенных еврейских братьев.
Указ Альгамбры ( также известный как Указ об изгнании) — указ, изданный 31 марта 1492 года объединенными католическими монархами Испании ( Изабелла I Кастильская и Фердинанд II Арагонский ), предписывающий изгнание всех необращенных практикующих евреев из королевств. Кастилии и Арагона , в том числе со всех ее территорий и владений, к 31 июля того же года. [1] Основная цель изгнания состояла в том, чтобы устранить влияние необращенных евреев на тогдашнее большое количество новохристианских конверсо еврейского происхождения в Испании , чтобы гарантировать, что настоятель не поощрял последних к рецидиву и возвращению в иудаизм.
Более половины населения Испании еврейского происхождения обратилось в католицизм в результате религиозных антиеврейских преследований и погромов , произошедших в 1391 году. По оценкам, в результате указа Альгамбры и преследований в предыдущие годы общая численность населения Испании еврейского происхождения населения в то время более 200 000 евреев обратились в католицизм и первоначально остались в Испании. От 40 000 до 80 000 человек не обратились в католичество и были изгнаны из-за своего твердого стремления оставаться евреями. Из тех, кто был изгнан как необращенные евреи, неопределенное количество, тем не менее, обратилось в католицизм однажды за пределами Испании и в конечном итоге вернулось в Испанию через годы после изгнания [2] из-за трудностей, с которыми многие столкнулись при переселении. Многие испанские евреи, покинувшие Испанию как евреи, также сначала переехали в Португалию, где впоследствии были насильно обращены в католическую церковь в 1497 году.
Большинство евреев, покинувших Испанию как евреи, приняли гостеприимство султана Баязида II и после Указа Альгамбры переселились в Османскую империю , [3] где основали общины, открыто исповедующие еврейскую религию; они и их потомки известны как восточные сефарды .
В течение столетий после [4] испанских и португальских декретов некоторые из новохристианских конверсо еврейского происхождения начали эмигрировать из Португалии и Испании, расселившись до 1700-х годов по всей территории Западной Европы и неиберийских владений колониальной Америки (в основном голландцев). королевства, включая Кюрасао в голландской Вест-Индии, Ресифи в голландских районах колониальной Бразилии , которые в конечном итоге были возвращены португальцами, и Новый Амстердам , который позже стал Нью-Йорком), образуя общины и формально возвращаясь к иудаизму. Именно коллектив этих общин и их потомки, известные как западные сефарды , и являются предметом данной статьи.
Поскольку первые члены западных сефардов состояли из людей, которые сами (или чьи непосредственные предки) лично пережили переходный период в качестве новых христиан, что привело к непрекращающимся судам и преследованиям криптоиудаизма со стороны португальской и испанской инквизиций , ранняя община продолжала к этому будет прибавляться дальнейшая новохристианская эмиграция, непрерывным потоком хлынувшая с Пиренейского полуострова в период с 1600-х по 1700-е годы. Новые христиане еврейского происхождения официально считались христианами из-за их насильственного или насильственного обращения; как таковые они подпадали под юрисдикцию инквизиторской системы католической церкви и подвергались суровым законам о ереси и отступничестве, если продолжали исповедовать свою исконную еврейскую веру. Те новые христиане, которые в конечном итоге покинули иберийскую культурную сферу и юрисдикцию инквизиции, смогли официально вернуться в иудаизм и открыть еврейскую практику, как только они оказались в своей новой толерантной среде убежища.
Как бывшие конверсос или их потомки, западные сефарды разработали особый ритуал, основанный на остатках иудаизма до изгнания из Испании, который некоторые практиковали тайно в то время, когда были новыми христианами, и находились под влиянием иудаизма, практиковавшегося общинами (в том числе евреи-сефарды Османской империи и евреи-ашкенази ), которые помогли им вновь принять нормативный иудаизм; а также испанско-марокканскими и итальянскими еврейскими обрядами, практикуемыми раввинами и хазанимами, набранными из этих общин для обучения их ритуальной практике. Более того, отчасти их самобытность как еврейской группы проистекает из того факта, что они считали себя вынужденными «переопределить свою еврейскую идентичность и обозначить ее границы [...] с помощью интеллектуальных инструментов, которые они приобрели в ходе христианской социализации» [ 5] во время их пребывания в качестве новохристианских конверсос.

Основные общины «западно-сефардских евреев» развивались в Западной Европе, Италии и неиберийских регионах Америки.
В дополнение к термину «западные сефарды», эту подгруппу евреев-сефардов иногда также называют «испанскими и португальскими евреями», «испанскими евреями», «португальскими евреями» или «евреями португальской нации».
Термин «западные сефарды» часто используется в современной исследовательской литературе для обозначения «испанских и португальских евреев», но иногда также и «испанско- марокканских евреев ».
Использование терминов «португальские евреи» и «евреи португальской нации» в таких регионах, как Нидерланды , Гамбург, Скандинавия и одно время в Лондоне, по-видимому, возникло прежде всего как способ «испанских и португальских евреев» «чтобы дистанцироваться от Испании во времена политической напряженности и войны между Испанией и Нидерландами в 17 веке. Подобные соображения, возможно, сыграли роль и для этнических евреев-сефардов во французских регионах Байонна и Бордо , учитывая их близость к испанской границе.
Другая причина использования терминологии «португальских» евреев, возможно, заключалась в том, что относительно большая часть рассматриваемых семей считала Португалию непосредственной отправной точкой с Пиренейского полуострова, даже если их более отдаленное семейное происхождение было испанским, а не португальским, поскольку Португалия был первым местом убежища и транзитным пунктом для многих испанских евреев сразу после их изгнания из Испании.
Поскольку термин «сефарды» (когда он используется в его этническом смысле) обязательно означает связь с Испанией, отличительной чертой западной подгруппы была дополнительная связь с Португалией. Таким образом, как подмножество сефардов, «португальцы» и «испанцы и португальцы» могли использоваться как синонимы. Наконец, почти все организованные сообщества этой группы традиционно использовали португальский, а не испанский в качестве официального или рабочего языка.
В Италии часто используется термин «испанские евреи» ( Ebrei Spagnoli ), но он включает в себя потомков евреев, изгнанных как евреи из Неаполитанского королевства , а также собственно «испанских и португальских евреев» (т.е. евреев, произошедших от бывших conversos и их потомки).
В Венеции испанских и португальских евреев часто называли «понентийскими» (западными), чтобы отличить их от «левантийских» (восточных) сефардов из районов Восточного Средиземноморья. Иногда итальянские евреи различают «португальских евреев» Пизы и Ливорно и «испанских евреев» Венеции, Модены и других мест.
Ученый Джозеф Дэн отличает «средневековых сефардов» (испанских изгнанников в Османскую империю 15 и 16 веков, прибывших как евреи) от «сефардов эпохи Возрождения» (бывших испанских и португальских общин конверсо, прибывших как новые христиане) в отношении соответствующих время формирующих контактов каждой группы с испанским языком и культурой.
Термин «сефарды» означает «испанский» или «латиноамериканец» и происходит от Сефарада , библейского места. Местоположение библейской Сефарады оспаривается, но Сефарад был идентифицирован более поздними евреями как Испания , то есть Пиренейский полуостров . Сефарад до сих пор означает «Испания» на современном иврите .
Отношения между общинами сефардского происхождения проиллюстрированы на следующей диаграмме :
«Сефарды» правильно относятся ко всем евреям, чьи семьи имеют обширную историю в Испании и Португалии , в отличие от евреев-ашкенази и всех других еврейских этнических групп . Однако евреев-мизрахи , имеющих обширную историю на Большом Ближнем Востоке и в Северной Африке, часто называют «сефардами» в более широком смысле в разговорной и религиозной речи из-за схожих стилей литургии и определенного количества смешанных браков между ними и собственно сефардами.
Основным фактором, отличающим «испанских и португальских евреев» (западных сефардов) от других «собственно сефардов», является то, что «испанские и португальские евреи» относятся конкретно к тем евреям, которые происходят от людей, чья история была практикующими членами еврейских общин, происходящих из Иберийского региона. полуостров был прерван периодом существования новых христиан (также известных как conversos , испанский термин, обозначающий «обращенных» в католицизм; или cristãos-novos , «новые христиане» в португальском эквиваленте) или анусимов (на иврите тех, кто «принужден» перейти из иудаизма в другую веру).
В период своего пребывания в качестве новых христиан многие конверсос продолжали исповедовать свою иудейскую веру втайне, насколько это было возможно. Тех новохристианских конверсос еврейского происхождения, которые тайно придерживались криптоеврейских обычаев, старохристианские испанцы и португальцы называли марранами (по-испански «свиньи») .
И наоборот, те новые христианские conversos, которые с того времени остались conversos, как те, кто находился на Пиренейском полуострове, так и те, кто переселился в иберийские колониальные владения во время испанской колонизации Америки , стали родственными сефардским Бней Анусим . Сефардские бней-анусим являются современными и в основном номинально христианскими потомками ассимилированных сефардских анусимов 15-го века и сегодня являются полностью ассимилированной подгруппой среди христианского населения иберийского происхождения в Испании, Португалии, латиноамериканской Америке и Бразилии. По историческим причинам и обстоятельствам сефардские Бней Анусим не вернулись к еврейской вере за последние пять столетий. [6] В наше время некоторые из них начали публично проявляться во все большем количестве, особенно в последние два десятилетия.
Для «испанских и португальских евреев» (западных сефардов) исторический период в качестве conversos сформировал их идентичность, культуру и обычаи. В этом отношении они явно отличаются от тех сефардов, которые происходят от евреев, покинувших Иберию как евреи до истечения срока действия Указа Альгамбры , повлекшего за собой изгнание в 1492 году из Испании и в 1497 году изгнание из Португалии всех некрещеных евреев. в католическую веру. Эти изгнанные евреи поселились в основном в Средиземноморском бассейне Южной Европы, Северной Африки и Ближнего Востока, а именно в Салониках , на Балканах и в Турции , и они стали восточными сефардами и североафриканскими сефардами соответственно. На протяжении веков сефардские еврейские общины под властью Османской империи обеспечивали духовное руководство рассеянным сефардам посредством своего вклада в литературу Респонса . [7] [8] [9] Эти сефардские общины предлагали убежище всем евреям, в том числе новохристианским конверсо сефардского еврейского происхождения, спасавшимся от инквизиции по всей Европе, а также их восточноевропейским единоверцам -ашкенази, спасавшимся от погромов.
Общей чертой, разделяющей западных сефардов («испанские и португальские евреи») с сефардскими бней-анусимами и нео-западными сефардами, является то, что все трое произошли от конверсос. «Западные сефарды» являются потомками бывших конверсос прошлых столетий; «Сефарды Бней Анусим» до сих пор номинально являются христианскими потомками конверсос; и «неозападные сефарды» - это растущее число современных бывших обращенных, которые в настоящее время возвращаются в иудаизм из числа сефардского населения Бней-Анусим.
Отличительным фактором между «западными сефардами» и зарождающимися «нео-западными сефардами» являются временные рамки возвращения к иудаизму, место возвращения, а также шаткие религиозные и юридические обстоятельства, окружающие их возвращение, включая препятствия и преследования. Таким образом, потомки конверсо, ставшие западными сефардами, вернулись в иудаизм между 16 и 18 веками, они сделали это еще до отмены инквизиции в 19 веке, и эти временные рамки вызвали необходимость их миграции из иберийской культурной среды. сфера. И наоборот, потомки конверсо, которые сегодня становятся зарождающимися нео-западными сефардами, вернулись в иудаизм между концом 20-го и началом 21-го веков, они делали это сразу после отмены инквизиции в 19-м веке, и это временные рамки не вызвали необходимости их миграции из иберийской культурной сферы.
Хотя еврейские общины были восстановлены в Испании и Португалии в конце 19-го и начале 20-го веков, в основном с помощью общин испанских и португальских евреев, таких как община в Лондоне, эти современные евреи в Португалии и евреи в Испании отличаются друг от друга. от «испанских и португальских евреев», поскольку по большей части современные еврейские общины, проживающие в Испании и Португалии, также включают другие еврейские этнические подразделения, недавно иммигрировавшие в Испанию и Португалию, такие как евреи-ашкенази Северной Европы.
In modern Iberia, practicing Jews of Sephardic origins, such as the Jewish community of Oporto, however, are also not Western Sephardim, but are Neo-Western Sephardim, as they were re-established in the 20th century and early 21st centuries with a campaign of outreach to the crypto-Jews of Sephardic Bnei Anusim origins. The Oporto community's return to Judaism was led by the returnee to Judaism Captain Artur Carlos de Barros Basto (1887–1961), known also as the "apostle of the Marranos". In 1921, realizing that there were less than twenty Ashkenazi Jews living in Porto, and that recent returnees to Judaism like himself were not organized and had to travel to Lisbon for religious purposes whenever necessary, Barros Basto began to think about building a synagogue and took initiative in 1923 to officially register the Jewish Community of Porto and the Israelite Theological Center in the city council of Porto. As mentioned, these communities of modern-day returnees to Judaism are among the first in the emergence of the nascent Neo-Western Sephardim. Neo-Western Sephardim are the modern returnees to Judaism throughout Iberia and Ibero-America emerging from among the population of Sephardic Bnei Anusim, and are distinct from Western Sephardim (those termed "Spanish and Portuguese Jews").
Even more recent examples of such Neo-Western Sephardim communities include the Belmonte Jews in Portugal, and the Xuetes of Spain. In the case of the Xuetes, the entire community of converso descendants was extended a blanket recognition as Jews by Rabbinical authorities in Israel due to their particular historical circumstances on the island which effectively resulted in a strict social isolation of the Xuetes imposed upon them by their non-Jewish-descended neighbors up until modern times.[10]
In the last five to ten years, "organized groups of [Sephardic] Benei Anusim have been established in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Chile, Ecuador, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Venezuela, and in Sefarad [the Iberian Peninsula] itself". Some members of these communities have formally reverted to Judaism.[11]
In 2015, the Spanish government enacted a law conceding Spanish nationality to the descendants of Sephardic Jews of Spanish origin. The law created a powerful incentive for the descendants of B'nei Anusim to re-discover their Sephardic ancestry, and it spurred a wave of genealogical inquiry and even genetic research. The law remained in force until 2019, therefore applications for Spanish citizenship on the basis of Sephardic ancestry are no longer accepted by the Spanish authorities.
Spanish and Portuguese Jews were originally descended from New Christian conversos (i.e. Jews converted to Roman Catholic Christianity) whose descendants later left the Iberian peninsula and reverted to Judaism.
Although legend has it that conversos existed as early as the Visigothic period, and that there was a continuous phenomenon of crypto-Judaism from that time lasting throughout Spanish history, this scenario is unlikely, as in the Muslim period of Iberia there was no advantage in passing as a Christian instead of publicly acknowledging one was a Jew. The main wave of conversions, often forced, followed the Massacre of 1391 in Spain. Legal definitions of that era theoretically acknowledged that a forced baptism was not a valid sacrament, but the Church confined this to cases where it was literally administered by physical force: a person who had consented to baptism under threat of death or serious injury was still regarded as a voluntary convert, and accordingly forbidden to revert to Judaism.[12] Crypto-Judaism as a large-scale phenomenon mainly dates from that time.
Conversos, whatever their real religious views, often (but not always) tended to marry and associate among themselves. As they achieved prominent positions in trade and in the Royal administration, they attracted considerable resentment from the "Old Christians". The ostensible reason given for issuance of the 1492 Alhambra Decree for the conversion, expulsion or execution of the unconverted Jews from Spain was that the unconverted Jews had supported the New Christian conversos in the crypto-Jewish practices of the latter, thus delaying or preventing their assimilation into the Christian community.
After the issuance of Spain's Alhambra Decree in 1492, a large proportion of the unconverted Jews chose exile rather than conversion, many of them crossing the border to Portugal. In Portugal, however, the Jews were again issued with a similar decree just a few years later in 1497, giving them the choice of exile or conversion. Unlike in Spain, however, in actual practice Portugal mostly prevented them from leaving, thus they necessarily stayed as ostensible converts to Christianity whether they wished to or not, after the Portuguese King reasoned that by their failure to leave they accepted Christianity by default. For this reason, crypto-Judaism was far more prevalent in Portugal than in Spain, even though many of these families were originally of Spanish rather than Portuguese descent. Over time, however, most crypto-Jews both of Spanish and Portuguese ancestry had left Portugal by the 18th century.

Scholars are still divided on the typical religious loyalties of the conversos, in particular on whether they are appropriately described as "crypto-Jews". Given the secrecy surrounding their situation, the question is not easy to answer: probably the conversos themselves were divided, and could be ranged at different points between the possible positions. The suggested profiles are as follows:
For these reasons, there was a continuous flow of people leaving Spain and Portugal (mostly Portugal) for places where they could practise Judaism openly, from 1492 until the end of the 18th century. They were generally accepted by the host Jewish communities as anusim (forced converts), whose conversion, being involuntary, did not compromise their Jewish status.
Conversos of the first generation after the expulsion still had some knowledge of Judaism based on memory of contact with a living Jewish community. In later generations, people had to avoid known Jewish practices that might attract undesired attention: conversos in group 3 evolved a home-made Judaism with practices peculiar to themselves, while those in group 2 had a purely intellectual conception of Judaism based on their reading of ancient Jewish sources preserved by the Church such as the Vulgate Old Testament, the Apocrypha, Philo and Josephus. Both groups therefore needed extensive re-education in Judaism after reaching their places of refuge outside the peninsula. This was achieved with the help of
There are still Jewish communities in the North African exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla. These places, though treated in most respects as integral parts of Spain, escaped the Inquisition and the expulsion, so these communities regard themselves as the remnant of pre-expulsion Spanish Jewry.
As Sephardic Jewish communities were established in central and northern Italy, following the expulsion of the Jews from Spain in 1492 and from the Kingdom of Naples in 1533, these areas were an obvious destination for conversos wishing to leave Spain and Portugal. The similarity of the Italian language to Spanish was another attraction. Given their Christian cultural background and high level of European-style education, the new emigrants were less likely to follow the example of the 1492 expellees by settling in the Ottoman Empire, where a complete culture change would be required.[18]
On the other hand, in Italy they ran the risk of prosecution for Judaizing, given that in law they were baptized Christians; for this reason they generally avoided the Papal States. The Popes did allow some Spanish-Jewish settlement at Ancona, as this was the main port for the Turkey trade, in which their links with the Ottoman Sephardim were useful. Other states found it advantageous to allow the conversos to settle and mix with the existing Jewish communities, and to turn a blind eye to their religious status. In the next generation, the children of conversos could be brought up as fully Jewish with no legal problem, as they had never been baptized.
The main places of settlement were as follows:
On the whole, the Spanish and Portuguese Jews remained separate from the native Italian rite Jews, though there was considerable mutual religious and intellectual influence between the groups. In a given city, there was often an "Italian synagogue" and a "Spanish synagogue", and occasionally a "German synagogue" as well. Many of these synagogues have since merged, but the diversity of rites survived in modern Italy.
The Spanish Synagogue (Scola Spagnola) of Venice was originally regarded as the "mother synagogue" for the Spanish and Portuguese community worldwide, as it was among the earliest to be established, and the first prayer book was published there. Later communities, such as in Amsterdam, followed its lead on ritual questions. With the decline in the importance of Venice in the 18th century, the leading role passed to Livorno (for Italy and the Mediterranean) and Amsterdam (for western countries). Unfortunately, the Livorno synagogue – considered to be the most important building in town – was destroyed in the Second World War: a modern building was erected on the same site in 1958–1962.
Many merchants maintained a presence in both Italy and countries in the Ottoman Empire, and even those who settled permanently in the Ottoman Empire retained their Tuscan or other Italian nationality, so as to have the benefit of the capitulations of the Ottoman Empire. Thus, in Tunisia there was a community of Juifs Portugais, or L'Grana (Livornese), separate from, and regarding itself as superior to, the native Tunisian Jews (Tuansa). Smaller communities of the same kind existed in other countries, such as Syria, where they were known as Señores Francos. They were generally not numerous enough to establish their own synagogues, instead meeting for prayer in each other's houses.
In the 16th and early 17th centuries, conversos were also seeking refuge beyond the Pyrenees, settling in France at Saint-Jean-de-Luz, Tarbes, Bayonne, Bordeaux, Marseille, and Montpellier. They lived apparently as Christians; were married by Catholic priests; had their children baptized, and publicly pretended to be Catholics. In secret, however, they circumcised their children, kept Shabbat and feast-days as best they could and prayed together.
Henry III of France confirmed the privileges granted them by Henry II of France, and protected them against accusations. Under Louis XIII of France, the conversos of Bayonne were assigned to the suburb of Saint-Esprit. At Saint-Esprit, as well as at Peyrehorade, Bidache, Orthez, Biarritz, and Saint-Jean-de-Luz, they gradually avowed Judaism openly. In 1640 several hundred conversos, considered to be Jews, were living at Saint-Jean-de-Luz; and a synagogue existed in Saint-Esprit as early as 1660.
In pre-Revolutionary France, the Portuguese Jews were one of three tolerated Jewish communities, the other two being the Ashkenazi Jews of Alsace-Lorraine and the Jews of the former Papal enclave of Comtat Venaissin; all three groups were emancipated at the French Revolution. The third community originally had their own Provençal rite, but adopted the Spanish and Portuguese rite shortly after the French Revolution and the incorporation of Comtat Venaissin into France. Today there are still a few Spanish and Portuguese communities in Bordeaux and Bayonne, and one in Paris, but in all these communities (and still more among French Jews generally) any surviving Spanish and Portuguese Jews are greatly outnumbered by recent Sephardic migrants of North African origin.
During the Spanish occupation of the Netherlands, converso merchants had a strong trading presence there. When the Dutch Republic gained independence in 1581, the Dutch retained trading links with Portugal rather than Spain, as Spain was regarded as a hostile power. Since there were penal laws against Catholics,[19] and Catholicism was regarded with greater hostility than Judaism, New Christian conversos (technically Catholics, as that was the Christian tradition they were forced into) were encouraged by the Dutch to "come out" openly as Jews. Given the multiplicity of Protestant sects, the Netherlands was the first country in the Western world to establish a policy of religious tolerance. This made Amsterdam a magnet for conversos leaving Portugal.
There were originally three Sephardi communities: the first, Beth Jacob, already existed in 1610, and perhaps as early as 1602; Neve Shalom was founded between 1608 and 1612 by Jews of Spanish origin. The third community, Beth Israel, was established in 1618. These three communities began co-operating more closely in 1622. Eventually, in 1639, they merged to form Talmud Torah, the Portuguese Jewish Community of Amsterdam, which still exists today. The current Portuguese Synagogue, sometimes known as the "Amsterdam Esnoga", was inaugurated in 1675, of which Abraham Cohen Pimentel was the head Rabbi.
At first the Dutch conversos had little knowledge of Judaism and had to recruit rabbis and hazzanim from Italy, and occasionally Morocco and Salonica, to teach them. Later on Amsterdam became a centre of religious learning: a religious college Ets Haim was established, with a copious Jewish and general library. This library still exists. The transactions of the college, mainly in the form of responsa, were published in a periodical, Peri Ets Haim (see links below). There were formerly several Portuguese synagogues in other cities such as The Hague. Since the German occupation of the Netherlands in the Second World War and the mass killing of Jews by the Nazi regime, the Amsterdam synagogue is the only remaining synagogue of the Portuguese rite in the Netherlands: it serves a membership of about 600. On the other hand, the synagogue at the Hague survived the war undamaged; it is now the Liberal Synagogue and no longer belongs to the "Portuguese" community.
The position of Jews in the Spanish Netherlands (modern Belgium) was rather different.[20] Considerable numbers of conversos lived there, in particular in Antwerp. The Inquisition was not allowed to operate. Nevertheless, their practice of Judaism remained under cover and unofficial, as acts of Judaizing in Belgium could expose one to proceedings elsewhere in the Spanish possessions. Sporadic persecutions alternated with periods of unofficial toleration. The position improved somewhat in 1714, with the cession of the southern Netherlands to Austria, but no community was officially formed until the 19th century. There is a Portuguese synagogue in Antwerp; its members, like those of the Sephardic rite synagogues of Brussels, are now predominantly of North African origin, and few if any pre-War families or traditions remain.

There were Portuguese Jews living in Hamburg as early as the 1590s. Records attest to their having a small synagogue called Talmud Torah in 1627, and the main synagogue, Beth Israel, was founded in 1652. From the 18th century on, the Portuguese Jews were increasingly outnumbered by "German Jews" (Ashkenazim). By 1900, they were thought to number only about 400.
A small branch of the Portuguese community was located in Altona, with a congregation known as Neweh Schalom. Historically, however, the Jewish community of Altona was overwhelmingly Ashkenazi, as Altona belonged to the kingdom of Denmark, which permitted Jews of all communities to settle there when Hamburg proper still only admitted the Portuguese.
Spanish and Portuguese Jews had an intermittent trading presence in Norway until the early 19th century, and were granted full residence rights in 1844.[22] Today they have no separate organizational identity from the general (mainly Ashkenazi) Jewish community, though traditions survive in some families.
Around 1550, many Sephardi Jews travelled across Europe to find their haven in Poland, which had the largest Jewish population in the whole of Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries. For this reason there are still Polish Jewish surnames with a possible Spanish origin. However, most of them quickly assimilated into the Ashkenazi community and retained no separate identity.

There were certainly Spanish and Portuguese merchants, many of them conversos, in England at the time of Queen Elizabeth I; one notable marrano was the physician Roderigo Lopez. In the time of Oliver Cromwell, Menasseh Ben Israel led a delegation seeking permission for Dutch Sephardim to settle in England: Cromwell was known to look favourably on the request, but no official act of permission has been found. By the time of Charles II and James II, a congregation of Spanish and Portuguese Jews had a synagogue in Creechurch Lane. Both these kings showed their assent to this situation by quashing indictments against the Jews for unlawful assembly.[23] For this reason the Spanish and Portuguese Jews of England often cite 1656 as the year of re-admission, but look to Charles II as the real sponsor of their community.
.JPG/440px-Lauderdale_Road_Sephardic_Synagogue_(3).JPG)
Bevis Marks Synagogue was opened in 1701 in London. In the 1830s and 40s there was agitation for the formation of a branch synagogue in the West End, nearer where most congregants lived, but rabbis refused this on the basis of Ascama 1, forbidding the establishment of other synagogues within six miles of Bevis Marks. Dissident congregants, together with some Ashkenazim, accordingly founded the West London Synagogue in Burton Street in 1841. An official branch synagogue in Wigmore Street was opened in 1853. This moved to Bryanston Street in the 1860s, and to Lauderdale Road in Maida Vale in 1896. A private synagogue existed in Islington from 1865 to 1884, and another in Highbury from 1885 to 1936. A third synagogue has been formed in Wembley. Over the centuries the community has absorbed many Sephardi immigrants from Italy and North Africa, including many of its rabbis and hazzanim. The current membership includes many Iraqi Jews and some Ashkenazim, in addition to descendants of the original families. The Wembley community is predominantly Egyptian.
The synagogues at Bevis Marks, Lauderdale Road and Wembley are all owned by the same community, formally known as Sahar Asamaim (Sha'ar ha-Shamayim), and have no separate organisational identities. The community is served by a team rabbinate: the post of Haham, or chief rabbi, is currently vacant (and has frequently been so in the community's history), the current head being known as the "Senior Rabbi". The day-to-day running of the community is the responsibility of a Mahamad, elected periodically and consisting of a number of parnasim (wardens) and one gabbay (treasurer). Under the current Senior Rabbi, Joseph Dweck, the name of the community has been changed from "Congregation of Spanish and Portuguese Jews" to "S&P Sephardi Community".[24]
.jpg/440px-Manchester_Jewish_Museum_(geograph_4749574).jpg)
In addition to the three main synagogues, there is the Montefiore Synagogue at Ramsgate associated with the burial place of Moses Montefiore. A synagogue in Holland Park is described as "Spanish and Portuguese" but serves chiefly Greek and Turkish Jews, with a mixed ritual: it is connected to the main community by a Deed of Association. The Manchester Sephardic synagogues are under the superintendence of the London community and traditionally used a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese ritual, which is giving way to a Jerusalem Sephardic style: the membership is chiefly Syrian in heritage, with some Turkish, Iraqi and North African Jews. The London community formerly had oversight over some Baghdadi synagogues in the Far East, such as the Ohel Leah Synagogue in Hong Kong and Ohel Rachel Synagogue in Shanghai. An informal community using the Spanish and Portuguese rite, and known as the "Rambam Synagogue", exists in Elstree and a further minyan has been established in Hendon. Newer Sephardic rite synagogues in London, mostly for Baghdadi and Persian Jews, preserve their own ritual and do not come under the Spanish and Portuguese umbrella.
Like the Amsterdam community, the London Spanish and Portuguese community early set up a Medrash do Heshaim (Ets Haim). This is less a functioning religious college than a committee of dignitaries responsible for community publications, such as prayer books.[25] In 1862 the community founded the "Judith Lady Montefiore College" in Ramsgate, for the training of rabbis. This moved to London in the 1960s: students at the college concurrently followed courses at Jews' College (now the London School of Jewish Studies). Judith Lady Montefiore College closed in the 1980s, but was revived in 2005 as a part-time rabbinic training programme run from Lauderdale Road, serving the Anglo-Jewish Orthodox community in general, Ashkenazim as well as Sephardim.[26]
From the 16th to the 18th centuries, a majority of conversos leaving Portugal went to Brazil. This included economic emigrants with no interest in reverting to Judaism. As the Inquisition was active in Brazil as well as in Portugal, conversos still had to be careful.
Dutch Sephardim were interested in colonisation, and formed communities in both Curaçao and Paramaribo, Suriname. Between 1630 and 1654, a Dutch colony existed in the north-east of Brazil, including Recife. This attracted both conversos from Portuguese Brazil and Jewish emigrants from Holland, who formed a community in Recife called Kahal Zur Israel Synagogue, the first synagogue in the Americas. On the reconquest of the Recife area by Portugal, many of these Jews (it is not known what percentage) left Brazil for new or existing communities in the Caribbean such as Curaçao. Others formed a new community, Congregation Shearith Israel, in New Amsterdam (later renamed as New York) in 1654, the first Jewish synagogue in what became the United States. Numerous conversos, however, stayed in Brazil. They survived by migrating to the countryside in the province of Paraíba and away from the reinstated Inquisition, which was mostly active in the major cities.
In the Caribbean, there were at one point Spanish and Portuguese synagogues in various other Dutch- and English-controlled islands, such as Jamaica, St. Thomas, Barbados, St. Eustatius and Nevis. With the elimination of the Inquisition after the Spanish American wars of independence, which many Caribbean Sephardim had supported, many of these communities declined as Jews took advantage of their new-found freedom to move to the mainland, where there were better economic opportunities. Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica and Honduras, among others, received numbers of Sephardim. Within a couple of generations, these immigrants mostly converted to Catholicism to better integrate into society. In the 21st century among the Caribbean islands, only Curaçao and Jamaica still have communities of Spanish and Portuguese Jews.[citation needed]
In Canada, at that time named as 'New France', Esther Brandeau was the first Jew to immigrate to Canada, in 1738, disguised as a Roman Catholic boy. She came from Saint-Esprit, a district of Bayonne, a port city in Southwestern France, where Spanish and Portuguese Jews had settled.[citation needed]
In the British Thirteen Colonies, synagogues were formed before the American Revolution at Newport, Rhode Island and Philadelphia, as well as in cities of the southern colonies of South Carolina, Virginia, and Georgia. Since then, many of the former Sephardic synagogues in the southern states and the Caribbean have become part of the Conservative, Reform or Reconstructionist movements, and retain only a few Spanish and Portuguese traditions. Thus, among the pioneers of the Reform Judaism movement in the 1820s there was the Sephardic congregation Beth Elohim in Charleston, South Carolina.[27]
Despite the Dutch origins of the New York community, by the 19th century all of the Spanish and Portuguese Jewish communities in the United States and Canada were very much part of the London-based family. The 19th and early 20th century editions of the prayer book published in London and Philadelphia contained the same basic text, and were designed for use on both sides of the Atlantic: for example, they all contained both a prayer for the Royal family and an alternative for use in republican states. The New York community continued to use these editions until the version of David de Sola Pool was published in 1954. On the other hand, in the first half of the 20th century, the New York community employed a series of hazzanim from Holland, with the result that the community's musical tradition remained close to that of Amsterdam.
_in_Manhattan,_New_York_City.jpg/440px-First_Cemetery_of_the_Spanish_and_Portuguese_Synagogue,_Shearith_Israel_(1656-1833)_in_Manhattan,_New_York_City.jpg)
There are only two remaining Spanish and Portuguese synagogues in the United States: Shearith Israel in New York, and Mikveh Israel in Philadelphia. In both congregations, only a minority of their membership has Western Sephardic ancestry, with the remaining members a mix of Ashkenazim, Levantine Sephardim, Mizrahim, and converts. Newer Sephardic and Sephardic-rite communities, such as the Syrian Jews of Brooklyn and the Greek and Turkish Jews of Seattle, do not come under the Spanish and Portuguese umbrella. The Seattle community did use the de Sola Pool prayer books until the publication of Siddur Zehut Yosef in 2002. Sephardic Temple Tifereth Israel, a community in Los Angeles with a mainly Turkish ethnic background, still uses the de Sola Pool prayer books.
The signing of the Treaty of Tordesillas of 1494, divided the world between Portugal, and Spain. Portugal was allotted responsibility over lands east of the Tordesillas meridian. In 1498 Vasco da Gama arrived on India's western coast where he was first greeted by a Polish Jew: Gaspar da Gama. In 1505 Portugal made Cochin its eastern headquarters, and in 1510 Goa was established as the capital of Portuguese India.
With the establishment of the Portuguese colonies in Asia, New Christians began flocking to India's western coast. Regarding Goa, the Jewish Virtual Library states that "From the early decades of the 16th century many New Christians from Portugal came to Goa. The influx soon aroused the opposition of the Portuguese and ecclesiastical authorities, who complained bitterly about the New Christians' influence in economic affairs, their monopolistic practices, and their secret adherence to Judaism."[28] Professor Walter Fischel of the University of California, Berkeley observes that despite the start of the inquisition in Portugal, the Portuguese relied heavily on Jews and New Christians in establishing their fledgling Asian empire.[29] The influence of Jews and New Christians in Goa was substantial. In his book, The Marrano Factory, Professor Antonio Saraiva of the University of Lisbon writes that "King Manuel theoretically abolished discrimination between Old and New Christians by the law of March 1, 1507 which permitted the departure of New Christians to any part of the Christian world, declaring that they 'be considered, favored and treated like the Old Christians and not distinct and separated from them in any matter.' Nevertheless, in apparent contradiction to that law, in a letter dated Almeirim, February 18, 1519, King Manuel promoted legislation henceforth prohibiting the naming of New Christians to the position of judge, town councilor or municipal registrar in Goa, stipulating, however, that those already appointed were not to be dismissed. This shows that even during the first nine years of Portuguese rule, Goa had a considerable influx of recently baptized Spanish and Portuguese Jews"[30] There are even examples of well-positioned Portuguese Jews, and New Christians, leaving the Portuguese administration to work with the Muslim sultanates of India in an attempt to strike back at Portugal for what it had done to them viz-a-viz the inquisition in Portugal.[31] Moises Orfali of Bar-Ilan University writes that the initially Portuguese colonial and ecclesiastical authorities complained in very strong terms about Jewish influence in Goa.[32] The Goa Inquisition which was established in 1560 was initiated by Jesuit Priest Francis Xavier from his headquarters in Malacca due to his inability to reanimate the faith of the New Christians there, Goa and in the region who had returned to Judaism. Goa became the headquarters of the Inquisition in Asia.
Cochin was, and still is, home to an ancient Jewish community (the Cochin Jews). Sephardic Jews from Iberia joined this community and became known as Paradesi Jews or "White Jews" (as opposed to older community which came to be known as the "Malabari Jews" or "Black Jews"). Cochin also attracted New Christians. In his lecture at the Library of Congress, Professor Sanjay Subrahmanyam of University of California, Los Angeles explains that New Christians came to India for economic opportunities (the Spice trade, the Golconda Diamonds trade, etc.) and because India had well-established Jewish communities which allowed them the opportunity to rejoin the Jewish world.[33]
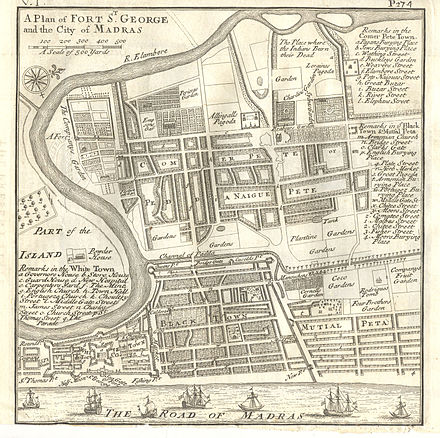
As explained by Professor Fischel, the Sephardic Jews of London were active in trading out of Fort St. George, India which later developed into the city of Madras, and is known today as Chennai and during the early years, the city council was required to have three Jewish aldermen to represent the community's interests.[34][35]
Malacca, Malaysia was in the 16th century a Jewish hub – not only for Portuguese Jews but also for Jews from the middle east and the Malabar. With its synagogues and rabbis, Jewish culture in Malacca was alive and well. Visible Jewish presence (Dutch Jews) existed in Malacca right up to the 18th century. Due to the inquisition a lot of the Jews of Malacca were either captured or assimilated into the Malacca-Portuguese (Eurasian) community where they continued to live as New Christians. Malacca was the headquarters of Jesuit priest Francis Xavier and it was his discovery of the conversos from Portugal there who had openly returned to Judaism as in the fortresses of India that became the turning point and from whence he wrote to King John III of Portugal to start the inquisition in the East. Prominent Malaccan Jewish figures include Portuguese Rabbi Manoel Pinto, who was persecuted by the Goa Inquisition in 1573 and Duarte Fernandes a former Jewish tailor who had fled Portugal to escape the Inquisition who became the first European to establish diplomatic relations with Thailand.

Most Spanish and Portuguese synagogues are, like those of the Italian and Romaniote Jews, characterised by a bipolar layout, with the tebáh bimah) near the opposite wall to the Hechál (Torah ark). The Hekhál has its parochet (curtain) inside its doors, rather than outside. The sefarim (Torah scrolls) are usually wrapped in a very wide mantle, quite different from the cylindrical mantles used by most Ashkenazi Jews. Tikim, wooden or metal cylinders around the sefarim, are typically not used. These were reportedly used, however, by the Portuguese Jewish community in Hamburg.
The most important synagogues, or esnogas, as they are usually called amongst Spanish and Portuguese Jews, are the Portuguese Synagogue of Amsterdam and those in London and New York. Amsterdam is still the historical centre of the Amsterdam minhag, as used in the Netherlands and former Dutch possessions such as Surinam. Also important is the Bevis Marks Synagogue in London, the historical centre of the London minhag. The Curaçao synagogue (built in 1732 and known as the Snoa, the Papiamento form of esnoga) of the Mikvé Israel-Emanuel congregation is considered one of the most important synagogues in the Jewish history of the Americas.
Since the late 20th century, many esnogas or synagogues in the Iberian Peninsula have been discovered by archaeologists and restored by both private and governmental efforts. In particular, the synagogues of Girona, Spain and Tomar, Portugal have been impressively restored to their former grandeur, if not their former social importance. (See the article Synagogue of Tomar.) Both Spain and Portugal have recently made efforts to reach out to descendants of Jews who were expelled from the peninsula in the 15th century, inviting them to apply for citizenship.
"Spanish and Portuguese Jews" typically spoke both Spanish and Portuguese in their Early Modern forms. This is in contrast to the languages spoken by Eastern Sephardim and North African Sephardim, which were archaic Old Spanish derived dialects of Judaeo-Spanish ("Ladino") and Haketia (a mixture of Old Spanish, Hebrew, and Aramaic, plus various other languages depending on the area of their settlement). Their Early Modern languages also differ from modern Spanish and Portuguese, as spoken by Sephardic Bnei Anusim of Iberia and Ibero-America, including some recent returnees to Judaism in the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
The use of Spanish and Portuguese languages by Western Sephardim persists in parts of the synagogue service. Otherwise, the use of Spanish and Portuguese quickly diminished amongst the Spanish and Portuguese Jews after the 17th century, when they were adapting to new societies.
In practice, from the mid-19th century on, the Spanish and Portuguese Jews gradually replaced their traditional languages with the local ones of their places of residence for their everyday use. Local languages used by "Spanish and Portuguese Jews" include Dutch in the Netherlands and Belgium, Low German in the Altona, Hamburg area, English in Great Britain, Ireland, Jamaica, and the United States, and Gascon, in its particular Judeo-Gascon sociolect, in France.[36]
In Curaçao, Spanish and Portuguese Jews contributed to the formation of Papiamento, a creole of Portuguese and various African languages. It is still used as an everyday language on the island.
Spanish and Portuguese Jews who have migrated to Latin America since the late 20th century have generally adopted modern standard Latin American varieties of Spanish as their mother tongue.
Because of the relatively high proportion of immigrants through Portugal, the majority of Spanish and Portuguese Jews of the 16th and 17th centuries spoke Portuguese as their first language. Portuguese was used for everyday communication in the first few generations, and was the usual language for official documents such as synagogue by-laws; for this reason, synagogue officers still often have Portuguese titles such as Parnas dos Cautivos and Thesoureiro do Heshaim. As a basic academic language, Portuguese was used for such works as the halakhic manual Thesouro dos Dinim by Menasseh Ben Israel and controversial works by Uriel da Costa.
The Judaeo-Portuguese dialect was preserved in some documents, but was extinct since the late 18th century: for example, Portuguese ceased to be a spoken language in Holland in the Napoleonic period, when Jewish schools were allowed to teach only in Dutch and Hebrew. Sermons in Bevis Marks Synagogue were preached in Portuguese till 1830, when English was substituted. Judaeo-Portuguese has had some influence on the Judeo-Italian language of Livorno, known as Bagitto.
Castilian Spanish was used as the everyday language by those who came directly from Spain in the first few generations. Those who came from Portugal regarded it as their literary language, as did the Portuguese at that time. Relatively soon, the Castilian Ladino took on a semi-sacred status ("Ladino", in this context, simply means literal translation from Hebrew: it should not be confused with the Judaeo-Spanish used by Balkan, Greek and Turkish Sephardim.) Works of theology as well as reza books (siddurim) were written in Castilian rather than in Portuguese; while, even in works written in Portuguese such as the Thesouro dos Dinim, quotations from the Bible or the prayer book were usually given in Spanish. Members of the Amsterdam community continued to use Spanish as a literary language. They established clubs and libraries for the study of modern Spanish literature, such as the Academia de los Sitibundos (founded 1676) and the Academia de los Floridos (1685).
In England the use of Spanish continued until the early 19th century: In 1740 Haham Isaac Nieto produced a new translation into contemporary Spanish of the prayers for the New Year and Yom Kippur, and in 1771 a translation of the daily, Sabbath and Festival prayers. There was an unofficial translation into English in 1771 by A. Alexander and others by David Levi in 1789 and following years, but the Prayer Books were first officially translated into English in 1836, by hakham David de Aaron de Sola. Today Spanish Jews in England have little tradition of using Spanish, except for the hymn Bendigamos, the translation of the Biblical passages in the prayer-book for Tisha B'Av, and in certain traditional greetings.
The Hebrew of the Spanish and Portuguese Jews from the 19th century and 20th century is characterised primarily by the pronunciation of בֿ (Beth rafé) as a hard b (e.g., Abrahám, Tebáh, Habdaláh) and the pronunciation of ע (ʿAyin) as a voiced velar nasal (Shemang, Ngalénu). The hard pronunciation of Beth Rafé differs from the v pronunciation of Moroccan Jews and the Judaeo-Spanish Jews of the Balkans, but is shared by Algerian and Syrian Jews. The nasal pronunciation of 'Ayin is shared with traditional Italian pronunciation (where it can be either "ng" or "ny"), but not with any other Sephardi groups.[37] Both these features are declining, under the influence of hazzanim from other communities and of Israeli Hebrew.
The sibilants ס, שׂ, שׁ and צ are all transcribed as s in earlier sources. This, along with the traditional spellings Sabá (Shabbat), Menasseh (Menashe), Ros(as)anáh (Rosh Hashana), Sedacáh (tzedaka), massoth (matzot), is evidence of a traditional pronunciation which did not distinguish between the various sibilants—a trait which is shared with some coastal dialects of Moroccan Hebrew.[38] Since the 19th century, the pronunciations [ʃ] (for שׁ and [ts] for צ have become common—probably by influence from Oriental Sephardic immigrants, from Ashkenazi Hebrew and, in our times, Israeli Hebrew.
The תֿ (taw rafé) is pronounced like t in all traditions of Spanish and Portuguese Jews today, although the consistent transliteration as th in 17th-century sources may suggest an earlier differentiation of תֿ and תּ. (Final תֿ is occasionally heard as d.)
In Dutch-speaking areas, but not elsewhere, ג (gimel) is often pronounced [χ] like Dutch "g". More careful speakers use this sound for gimel rafé (gimel without dagesh), while pronouncing gimel with dagesh as [ɡ].[39]
Dutch Sephardim take care to pronounce he with mappiq as a full "h", usually repeating the vowel: vi-yamlich malchutéhe.
The accentuation of Hebrew adheres strictly to the rules of Biblical Hebrew, including the secondary stress on syllables with a long vowel before a shva. Also, the shvá nang in the beginning of a word is normally pronounced as a short eh (Shemang, berít, berakháh). Shva nang is also normally pronounced after a long vowel with secondary stress (ngomedím, barekhú). However it is not pronounced after a prefixed u- (and): ubne, not u-bene.
Vocal shva, segol (short e) and tzere (long e) are all pronounced like the 'e' in "bed": there is no distinction except in length.[40] In some communities, e.g. Amsterdam, vocal shva is pronounced [a] when marked with gangya (a straight line next to the vowel symbol, equivalent to meteg), and as [i] when followed by the letter yodh: thus va-nashubah and bi-yom (but be-Yisrael).[41]
The differentiation between kamatz gadol and kamatz katan is made according to purely phonetic rules without regard to etymology, which occasionally leads to spelling pronunciations at variance with the rules laid down in the grammar books. For example, כָל (all), when unhyphenated, is pronounced "kal" rather than "kol" (in "kal ngatsmotai" and "Kal Nidre"), and צָהֳרַיִם (noon) is pronounced "tsahorayim" rather than "tsohorayim". This feature is shared by other Sephardic groups, but is not found in Israeli Hebrew. It is also found in the transliteration of proper names in the King James Version such as Naomi, Aholah and Aholibah.
Although all Sephardic liturgies are similar, each group has its own distinct liturgy. Many of these differences are a product of the syncretization of the Spanish liturgy and the liturgies of the local communities where Spanish exiles settled. Other differences are the result of earlier regional variations in liturgy from pre-expulsion Spain. Moses Gaster (died 1939, Hakham of the S&P Jews of Great Britain) has shown that the order of prayers used by Spanish and Portuguese Jews has its origin in the Castilian liturgy of Pre-Expulsion Spain.
As compared with other Sephardic groups, the minhag of the Spanish and Portuguese Jews is characterised by a relatively low number of cabbalistic additions. The Friday night service thus traditionally starts with Psalm 29, "Mizmor leDavid: Habu LaA.”. In the printed siddurim of the mid-17th century, “Lekhah Dodi" and the Mishnaic passage Bammeh madlikin are also not yet included, but these are included in all newer siddurim of the tradition except for the early West London and Mickve Israel (Savannah) Reform prayerbooks, both of which have Spanish and Portuguese roots.
Of other, less conspicuous, elements, a number of archaic forms can be mentioned—including some similarities with the Italian and Western Ashkenazi traditions. Such elements include the shorter form of the Birkat Hamazon which can be found in the older Amsterdam and Hamburg/Scandinavian traditions. The Livorno (Leghorn) tradition, however, includes many of the cabbalistic additions found in most other Sephardi traditions. The current London minhag is generally close to the Amsterdam minhag, but follows the Livorno tradition in some details—most notably in the Birkat Hamazon.
One interesting feature of the tradition (at least in New York and Philadelphia) is that, when reading the haftarah on Simhat Torah and Shabbat Bereshit, the Hatan Torah and Hatan Bereshit chant two extra verses pertaining to bridegrooms from Isaiah 61:10 and 62:5 at the end of the standard haftarot for the days themselves. This seems to be a unique remnant of the old tradition of reading Isaiah 61:10–63:9 if a bridegroom who had been married the previous week was present in synagogue.

The ritual music of the Spanish and Portuguese Jews differs from other Sephardic music in that it is influenced by Western European Baroque and Classical music to a relatively high degree. Not only in Spanish and Portuguese communities, but in many others in southern France[42] and northern Italy,[43] it was common to commission elaborate choral compositions, often including instrumental music, for the dedication of a synagogue, for family events such as weddings and circumcisions and for festivals such as Hoshana Rabbah, on which the halachic restriction on instrumental music did not apply.
Already in 1603, the sources tell us that harpsichords were used in the Spanish and Portuguese synagogues in Hamburg. Particularly in the Amsterdam community, but to some degree also in Hamburg and elsewhere, there was a flourishing of Classical music in the synagogues in the 18th century. There was formerly a custom in Amsterdam, inspired by a hint in the Zohar, of holding an instrumental concert on Friday afternoon prior to the coming in of the Shabbat, as a means of getting the congregants in the right mood for the Friday night service. An important Jewish composer was Abraham Caceres; music was also commissioned from non-Jewish composers such as Cristiano Giuseppe Lidarti, some of which is still used such has this aria from Lidarti's Oratorio Esther or this inaugural piece "Col Ansama" recorded live in Amsterdam's Royal Concertgebouw.
The same process took place in Italy, where the Venetian community commissioned music from non-Jewish composers such as Carlo Grossi and Benedetto Marcello.
Another important centre for Spanish and Portuguese Jewish music was Livorno, where a rich cantorial tradition developed, incorporating both traditional Sephardic music from around the Mediterranean and composed art music: this was in turn disseminated to other centres.[44]
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, in particular in Italy at the time of the Italian unification, hazzanim sometimes doubled as opera singers, and some liturgical compositions from this period reflect this operatic character.
Already in the 17th century, choirs were used in the service throughout the year in the Amsterdam community. In 1886 the Portuguese vocal society Santo Serviço was established. In 2005 this choir was re-established under the leadership of musical director Barry Mehler. Their debut was broadcast on national television (NOS). This custom was introduced in London in the early 19th century. In most cases, the choirs have consisted only of men and boys, but in Curaçao, the policy was changed to allow women in the choir (in a separate section) in 1863.
There are early precedents for the use of instrumental music in the synagogue originating in 17th century Italy as well as the Spanish and Portuguese communities of Hamburg and Amsterdam and in the Ashkenazic community of Prague. As in most other communities the use of instrumental music is not permitted on Shabbat or festivals.
As a general rule, Spanish and Portuguese communities do not use pipe organs or other musical instruments during services. In some Spanish and Portuguese communities, notably in France (Bordeaux, Bayonne), US (Savannah, Georgia, Charleston, South Carolina, Richmond, Virginia) and the Caribbean (Curaçao), pipe organs came into use during the course of the 19th century, in parallel with developments in Reform Judaism. In Curaçao, where the traditional congregation had an organ set up in the late 19th century, the use of the organ on Shabbat was eventually also accepted, as long as the organ player was not Jewish. In the more traditional congregations, such as London and New York, a free-standing organ or electric piano is used at weddings or benot mitzvah (although never on Shabbat or Yom Tob), in the same way as in some English Ashkenazi synagogues.
The cantorial style of the Spanish and Portuguese Jews adheres to the general Sephardi principle that every word is sung out loud and that most of the ritual is performed communally rather than soloistically (although nowadays in the New York community, the Pesukei dezimra (zemirot) throughout the year, Hallel on festivals or the new moon, and several of the selichot during Yom Kippur are chanted in a manner more similar to the Ashkenazi practice of reading only the first and last few verses of each paragraph aloud). The hazzan's role is typically one of guiding the congregation rather than being a soloist. Thus, there is traditionally a much stronger emphasis on correct diction and knowledge of the musical minhag than on the soloistic voice quality.[45] In the parts of the service where the ḥazzan would traditionally have a more soloistic role, the basic melodies are embellished according to the general principles of Baroque performance practice: for example, after a prayer or hymn sung by the congregation, the ḥazzan often repeats the last line in a highly elaborated form. Two- and three-part harmony is relatively common, and Edwin Seroussi has shown that the harmonies are a reflection of more complex, four-part harmonies in written sources from the 18th century.
The recitative style of the central parts of the service, such as the Amidah, the Psalms and the cantillation of the Torah is loosely related to that of other Sephardi and Mizraḥi communities, though there is no formal maqam system as used by most of these.[46] The closest resemblance is to the rituals of Gibraltar and Northern Morocco, as Spanish and Portuguese communities traditionally recruited their ḥazzanim from these countries. There is a remoter affinity with the Babylonian and North African traditions: these are more conservative than the Syrian and Judaeo-Spanish (Balkan, Greek, Turkish) traditions, which have been more heavily influenced by popular Mediterranean, Turkish and Arabic music.
In other parts of the service, and in particular on special occasions such as the festivals, Shabbat Bereshit and the anniversary of the founding of the synagogue, the traditional tunes are often replaced by metrical and harmonized compositions in the Western European style. This is not the case on Rosh Hashanah and Kippúr (Yom Kippur), when the whole service has a far more archaic character.
A characteristic feature of Oriental Sephardic music is the transposition of popular hymn tunes (themselves sometimes derived from secular songs) to important prayers such as Nishmat and Kaddish. This occurs only to a limited extent in the Spanish and Portuguese ritual: such instances as exist can be traced to the book of hymns Imre no'am (1628), published in Amsterdam by Joseph Gallego, a hazzan originating in Salonica.[47] Certain well-known tunes, such as El nora aliláh and Ahhot ketannáh, are shared with Sephardi communities worldwide with small variations.
Spanish and Portuguese traditional cantillation has several unique elements. Torah cantillation is divided into two musical styles. The first is the standard used for all regular readings. A similar but much more elaborate manner of cantillation is used on special occasions. This is normally referred to as High Tangamim or High Na'um. It is used for special portions of the Torah reading, principally the Ten Commandments[48] but also Chapter 1 of Bereshit (on Simchat Torah), the Shirat ha-Yam, the Song of Moses, the concluding sentences of each of the five books and several other smaller portions.[49]
Spanish and Portuguese Torah cantillation has been notated several times since the 17th century. The melodies now in use, particularly in London, show some changes from the earlier notated versions and a degree of convergence with the Iraqi melody.[50]
The rendition of the Haftarah (prophetic portion) also has two (or three) styles. The standard, used for most haftarot, is nearly identical with that of the Moroccan nusach. A distinctly more somber melody is used for the three haftarot preceding the ninth of Ab (the "three weeks".) On the morning of the Ninth of Ab a third melody is used for the Haftarah—although this melody is borrowed from the melody for the Book of Ruth.
There is a special melody used for reading the Book of Esther on Purim, but this is not cantillation in the accepted sense as it is chant-like and does not depend on the Masoretic symbols. There are however the remnants of a cantillation melody in the chant for the verses from the Book of Esther read at the conclusion of the morning service in the two weeks preceding Purim;[51] this melody is also used for certain verses recited by the congregation during the reading on Purim itself.
The books of Ruth, read on Shavuot, and Lamentations, read on the Ninth of Ab, have their own cantillation melodies as well. There is no tradition of reading Ecclesiastes.
Most Spanish and Portuguese communities have no tradition of liturgical reading of the Shir haShirim (Song of Songs), unlike Ashkenazim who read it on Pesach and Oriental Sephardim who read it on Friday nights. However, in the two weeks preceding Pesach a passage consisting of selected verses from that book is read each day at the end of the morning service.[52] The chant is similar but not identical to the chant for Shir haShirim in the Moroccan tradition, but does not exactly follow the printed cantillation marks. A similar chant is used for the prose parts of the book of Job on the Ninth of Ab.
There is no cantillation mode for the books of Psalms, Proverbs and the poetic parts of Job. The chant for the Psalms in the Friday night service has some resemblance to the cantillation mode of the Oriental traditions, but is not in any obvious way dependent on the cantillation marks.




{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: others (link)