Казахстан , [b] официально Республика Казахстан , [c] является страной, не имеющей выхода к морю , в основном в Центральной Азии , с частью в Восточной Европе . [d] Он граничит с Россией на севере и западе , Китаем на востоке , Кыргызстаном на юго-востоке , Узбекистаном на юге и Туркменистаном на юго-западе , с береговой линией вдоль Каспийского моря . Его столица - Астана , в то время как крупнейший город и ведущий культурный и торговый центр - Алматы . Казахстан является девятой по величине страной в мире по площади суши и крупнейшей страной, не имеющей выхода к морю. Его население составляет 20 миллионов человек, а плотность населения - одна из самых низких в мире, менее 6 человек на квадратный километр (16 человек/кв. милю). [14] Этнические казахи составляют большинство, в то время как этнические русские составляют значительное меньшинство. Официально светский Казахстан является страной с мусульманским большинством и значительной христианской общиной .
Казахстан был заселен с эпохи палеолита . В древности на этой территории доминировали различные кочевые иранские народы, такие как саки , массагеты и скифы , а Ахеменидская персидская империя расширялась в сторону южного региона. Тюркские кочевники вошли в регион еще в шестом веке. В 13 веке эта территория была покорена Монгольской империей под предводительством Чингисхана . После распада Золотой Орды в 15 веке на территории, примерно соответствующей современному Казахстану, было создано Казахское ханство . К 18 веку Казахское ханство распалось на три жуза (племенные подразделения), которые постепенно были поглощены и завоеваны Российской империей ; к середине 19 века весь Казахстан номинально находился под властью России. [15] После русской революции 1917 года и последующей гражданской войны в России территория была реорганизована несколько раз. В 1936 году были установлены его современные границы с образованием Казахской Советской Социалистической Республики в составе Советского Союза . Казахстан был последней республикой в составе Советского Союза, объявившей о независимости в 1991 году во время его распада .
Казахстан доминирует в Центральной Азии как в экономическом, так и в политическом плане , составляя 60 процентов ВВП региона , в первую очередь за счет своей нефтегазовой промышленности ; он также обладает огромными минеральными ресурсами. [16] Казахстан также имеет самый высокий рейтинг индекса человеческого развития в регионе. Это унитарная конституционная республика; [17] однако его правительство является авторитарным . [18] [19] Тем не менее, после отставки Нурсултана Назарбаева в 2019 году, который руководил страной с момента обретения независимости, были предприняты дополнительные усилия по демократизации и политическим реформам. Казахстан является государством-членом Организации Объединенных Наций , Всемирной торговой организации , Содружества Независимых Государств , Шанхайской организации сотрудничества , Евразийского экономического союза , Организации Договора о коллективной безопасности , Организации по безопасности и сотрудничеству в Европе , Организации исламского сотрудничества , Организации тюркских государств и Международной организации тюркской культуры .
Английское слово «Kazakh» , означающее представителя казахского народа, происходит от русского слова « казах» . [20] Родное название — казахский : қазақ , романизированное : qazaq . Оно может происходить от тюркского глагола qaz- , «бродить», отражающего кочевую культуру казахов. [21] Термин « Казак » имеет то же происхождение. [21]
В тюрко-персидских источниках термин Özbek-Qazaq впервые появился в середине XVI века в « Тарих-и-Рашиди» Мирзы Мухаммада Хайдара Дуглата , чагатаидского принца Кашмира , который помещает казахов в восточную часть Дешт-и Кыпчака . [22] По словам Василия Бартольда , казахи, вероятно, начали использовать это название в XV веке. [23]
Хотя традиционно термин «казах» относился только к этническим казахам , включая тех, кто проживает в Китае, России, Турции, Узбекистане и других соседних странах, этот термин все чаще используется для обозначения любого жителя Казахстана, включая представителей других национальностей. [24]

Казахстан был заселен со времен палеолита . [25] Ботайская культура (3700–3100 гг. до н.э.) считается первым одомашниванием лошадей. Ботайское население получило большую часть своей родословной от глубоко европейского населения, известного как Древние Северные Евразийцы , а также демонстрирует некоторую древневосточноазиатскую примесь. [26] Скотоводство развилось в эпоху неолита . Население было европеоидным в период бронзового и железного веков . [27] [28]
Казахская территория была ключевым компонентом Евразийского торгового степного пути , предка наземных Шелковых путей . Археологи полагают, что люди впервые одомашнили лошадь в обширных степях региона. В недавние доисторические времена Центральная Азия была заселена такими группами, как, возможно, индоевропейская афанасьевская культура , [29] позднее ранние индоиранские культуры, такие как андроновская , [30] и более поздние индоиранцы, такие как саки и массагеты . [31] [32] Другие группы включали кочевых скифов и персидскую империю Ахеменидов на южной территории современной страны. Было обнаружено, что андроновская и срубная культуры , предшественники народов скифских культур , имеют смешанное происхождение от скотоводов ямной степи и народов среднеевропейского среднего неолита. [33]
В 329 году до нашей эры Александр Македонский и его македонская армия сражались в битве при Яксарте со скифами на реке Яксарт, ныне известной как Сырдарья, вдоль южной границы современного Казахстана.

Основная миграция тюркских народов произошла между V и XI веками, когда они распространились по большей части Центральной Азии. Тюркские народы медленно вытесняли и ассимилировали прежних ираноязычных местных жителей, превратив население Центральной Азии из преимущественно иранского в преимущественно восточноазиатского происхождения. [34]
Первый Тюркский каганат был основан Бумином в 552 году на Монгольском нагорье и быстро распространился на запад к Каспийскому морю. Гёктюрки гнали перед собой различные народы: хионитов , уаров , огуров и других. Они, по-видимому, слились с аварами и булгарами . В течение 35 лет восточная половина и Западный Тюркский каганат стали независимыми. Западный каганат достиг своего пика в начале 7-го века.
Куманы вошли в степи современного Казахстана примерно в начале XI века, где они позже объединились с кипчаками и основали обширную конфедерацию половцев и кипчаков. В то время как древние города Тараз (Аулие-Ата) и Хазрат-и Туркестан долгое время служили важными промежуточными станциями на Шелковом пути, соединяющем Азию и Европу, настоящая политическая консолидация началась только с монгольским правлением в начале XIII века. Во времена Монгольской империи были созданы первые строго структурированные административные округа (улусы). После раздела Монгольской империи в 1259 году земля, которая станет современным Казахстаном, попала под власть Золотой Орды , также известной как Улус Джучи. В период Золотой Орды среди правящей элиты возникла тюрко-монгольская традиция , в соответствии с которой тюркизированные потомки Чингисхана следовали исламу и продолжали править землями.
В 1465 году в результате распада Золотой Орды возникло Казахское ханство . Основанное Джанибек-ханом и Керей-ханом , оно продолжало находиться под властью тюрко-монгольского клана Торе ( династия Джучидов ). На протяжении всего этого периода в степи продолжали доминировать традиционный кочевой образ жизни и скотоводческая экономика . В 15 веке среди тюркских племен начала формироваться отчетливая казахская идентичность . За этим последовала казахская война за независимость , в ходе которой ханство обрело суверенитет от Шейбанидов . Этот процесс был закреплен к середине 16 века с появлением казахского языка , культуры и экономики.

Тем не менее, регион был в центре все возрастающих споров между коренными казахскими эмирами и соседними персоязычными народами на юге. На пике своего развития ханство управляло частями Средней Азии и контролировало Куманию . Территории Казахского ханства расширялись вглубь Центральной Азии. К началу 17 века Казахское ханство боролось с влиянием племенных распрей, которые фактически разделили население на Большую, Среднюю и Малую (или Малую) орды ( жузы ). Политическая раздробленность, племенные распри и уменьшающаяся важность сухопутных торговых путей между востоком и западом ослабили Казахское ханство. Хивинское ханство воспользовалось этой возможностью и присоединило полуостров Мангышлак . Узбекское правление там длилось два столетия до прихода русских.
В течение 17-го века казахи воевали с ойратами , федерацией западных монгольских племен, включая джунгар . [35] Начало 18-го века ознаменовало зенит Казахского ханства. В этот период Младшая Орда участвовала в войне 1723–1730 годов против Джунгарского ханства , после их «Великого бедствия» вторжения на казахскую территорию. Под руководством Абулхаир-хана казахи одержали крупные победы над джунгарами на реке Буланты в 1726 году и в битве при Аныракае в 1729 году. [36]
Аблай-хан участвовал в самых значительных сражениях против джунгар с 1720-х по 1750-е годы, за что был объявлен народом « батыром » («героем»). Казахи страдали от частых набегов на них волжских калмыков . Кокандское ханство использовало слабость казахских жузов после набегов джунгар и калмыков и завоевало нынешний Юго-Восточный Казахстан, включая Алматы , формальную столицу в первой четверти 19 века. Бухарский эмират правил Шымкентом до того, как русские получили господство. [37]


В первой половине XVIII века Российская империя построила Иртышскую линию , серию из сорока шести фортов и девяноста шести редутов, включая Омск (1716), Семипалатинск (1718), Павлодар (1720), Оренбург (1743) и Петропавловск (1752), [38] чтобы предотвратить набеги казахов и ойратов на территорию России. [39] В конце XVIII века казахи воспользовались восстанием Пугачева , которое было сосредоточено в районе Волги, чтобы совершать набеги на русские и поволжские немецкие поселения. [40] В XIX веке Российская империя начала расширять свое влияние на Среднюю Азию. Период « Большой игры » обычно считается длившимся примерно с 1813 года до англо-русской конвенции 1907 года . Цари фактически правили большей частью территории, принадлежащей нынешней Республике Казахстан.
Российская империя ввела систему управления и построила военные гарнизоны и казармы в своих усилиях установить присутствие в Центральной Азии в так называемой «Большой игре» за господство в этом регионе против Британской империи , которая расширяла свое влияние с юга в Индию и Юго-Восточную Азию. Россия построила свой первый форпост, Орск , в 1735 году. Россия ввела русский язык во всех школах и правительственных организациях.
Попытки России навязать свою систему вызвали негодование казахов, и к 1860-м годам некоторые казахи сопротивлялись ее правлению. Россия нарушила традиционный кочевой образ жизни и животноводческую экономику, и люди страдали от голода, а некоторые казахские племена были уничтожены. Казахское национальное движение, начавшееся в конце 19 века, стремилось сохранить родной язык и идентичность, сопротивляясь попыткам Российской империи ассимилировать и задушить казахскую культуру.
Начиная с 1890-х годов все большее число переселенцев из Российской империи начало колонизировать территорию современного Казахстана, в частности, провинцию Семиречье . Число поселенцев еще больше возросло после завершения строительства Трансаральской железной дороги от Оренбурга до Ташкента в 1906 году. Специально созданное Переселенческое управление в Санкт-Петербурге курировало и поощряло миграцию для расширения российского влияния в этом районе. В течение 19 века около 400 000 русских иммигрировали в Казахстан, а около миллиона славян, немцев, евреев и других иммигрировали в регион в течение первой трети 20 века. [41] Василий Балабанов был администратором, ответственным за переселение в течение большей части этого времени.
Конкуренция за землю и воду, которая последовала между казахами и пришельцами, вызвала большое негодование против колониального правления в последние годы существования Российской империи . Самое серьезное восстание, Среднеазиатское восстание , произошло в 1916 году. Казахи напали на русских и казачьих поселенцев и военные гарнизоны. Восстание привело к серии столкновений и жестоким расправам, совершенным обеими сторонами. [42] Обе стороны сопротивлялись коммунистическому правительству до конца 1919 года.


После краха центрального правительства в Петрограде в ноябре 1917 года казахи (тогда в России официально именуемые «киргизами») пережили краткий период автономии ( Алашская автономия ), прежде чем в конечном итоге поддаться власти большевиков . 26 августа 1920 года была создана Киргизская Автономная Социалистическая Советская Республика в составе Российской Советской Федеративной Социалистической Республики (РСФСР). Киргизская АССР включала территорию современного Казахстана, но ее административным центром был преимущественно населенный русскими город Оренбург . В июне 1925 года Киргизская АССР была переименована в Казахскую АССР , а ее административный центр был переведен в город Кызылорда , а в апреле 1927 года — в Алма-Ату .
Советские репрессии против традиционной элиты, наряду с принудительной коллективизацией в конце 1920-х и 1930-х годах, привели к голоду и высокой смертности, что привело к беспорядкам (см. также: Голод в Казахстане 1932–33 годов ). [43] [44] В 1930-х годах некоторые представители казахской интеллигенции были казнены — в рамках политики политических репрессий, проводимой советским правительством в Москве. [ необходима цитата ]
5 декабря 1936 года Казахская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика (территория которой к тому времени соответствовала территории современного Казахстана) была выделена из состава РСФСР и образована Казахская Советская Социалистическая Республика — полноправная союзная республика в составе СССР, одна из одиннадцати таких республик на тот момент, наряду с Киргизской Советской Социалистической Республикой .
Республика была одним из пунктов назначения для сосланных и осужденных лиц, а также для массовых переселений или депортаций, осуществлявшихся центральными властями СССР в 1930-х и 1940-х годах, например, около 400 000 немцев Поволжья были депортированы из Автономной Советской Социалистической Республики Немцев Поволжья в сентябре-октябре 1941 года, а затем позже греки и крымские татары . Депортированные и заключенные были интернированы в некоторых из крупнейших советских трудовых лагерей (ГУЛАГ), включая лагерь АЛЖИР за пределами Астаны, который был зарезервирован для жен мужчин, считавшихся «врагами народа». [45] Многие переехали из-за политики перемещения населения в Советском Союзе , а другие были вынуждены принудить себя к поселениям в Советском Союзе .

Советско -германская война (1941–1945) привела к росту индустриализации и добычи полезных ископаемых в поддержку военных усилий. Однако на момент смерти Иосифа Сталина в 1953 году Казахстан все еще имел преимущественно аграрную экономику. В 1953 году советский лидер Никита Хрущев инициировал кампанию по освоению целинных земель , призванную превратить традиционные пастбища Казахстана в крупный регион по производству зерна для Советского Союза. Политика освоения целинных земель принесла неоднозначные результаты. Однако, наряду с более поздними модернизациями при советском лидере Леониде Брежневе (у власти в 1964–1982 годах), она ускорила развитие сельскохозяйственного сектора, который остается источником средств к существованию для значительной части населения Казахстана. Из-за десятилетий лишений, войны и переселения к 1959 году казахи стали меньшинством, составляя 30 процентов населения. Этнические русские составляли 43 процента. [46]
В 1947 году СССР в рамках своего проекта по созданию атомной бомбы основал полигон для испытания атомной бомбы недалеко от северо-восточного города Семипалатинска , где в 1949 году было проведено первое испытание советской ядерной бомбы. До 1989 года были проведены сотни ядерных испытаний, имевших неблагоприятные последствия для окружающей среды и населения страны. [47] Антиядерное движение в Казахстане стало крупной политической силой в конце 1980-х годов.
В апреле 1961 года Байконур стал трамплином для «Востока-1» — космического корабля, на котором советский космонавт Юрий Гагарин стал первым человеком, вышедшим в космос.
В декабре 1986 года в Алматы прошли массовые демонстрации молодых этнических казахов, позже названные Желтоксанским бунтом, в знак протеста против замены Первого секретаря Коммунистической партии Казахской ССР Динмухамеда Кунаева на Геннадия Колбина из РСФСР . Правительственные войска подавили беспорядки, несколько человек были убиты, а многие демонстранты были заключены в тюрьму. [48] В последние дни советской власти недовольство продолжало расти и нашло выражение в политике гласности («открытости») советского лидера Михаила Горбачева .
25 октября 1990 года Казахстан объявил о своем суверенитете на своей территории как республики в составе Советского Союза. После неудачной попытки государственного переворота в Москве в августе 1991 года Казахстан объявил о своей независимости 16 декабря 1991 года, став последней советской республикой, объявившей о своей независимости. Десять дней спустя прекратил свое существование и сам Советский Союз .
Лидер коммунистической эпохи Казахстана Нурсултан Назарбаев стал первым президентом страны. Назарбаев правил авторитарно. Акцент был сделан на преобразовании экономики страны в рыночную, в то время как политические реформы отставали от экономических достижений. К 2006 году Казахстан производил 60 процентов ВВП Центральной Азии, в основном за счет своей нефтяной промышленности. [16]
В 1997 году правительство перенесло столицу в Астану , переименованную в Нур-Султан 23 марта 2019 года, [49] из Алматы , крупнейшего города Казахстана, где она была основана во времена Советского Союза. [50] Выборы в Мажилис в сентябре 2004 года привели к тому, что в нижней палате доминировала проправительственная партия «Отан» во главе с президентом Назарбаевым. Две другие партии, считающиеся симпатизирующими президенту, включая аграрно-промышленный блок АИСТ и партию «Асар» , основанную дочерью президента Назарбаева, получили большинство оставшихся мест. Оппозиционные партии, которые были официально зарегистрированы и участвовали в выборах, получили одно место. Организация по безопасности и сотрудничеству в Европе наблюдала за выборами, которые, по ее словам, не соответствовали международным стандартам. [51]
В марте 2011 года Назарбаев обрисовал прогресс, достигнутый Казахстаном на пути к демократии. [52] По состоянию на 2010 год [update]Казахстан был отмечен в Индексе демократии журнала The Economist как авторитарный режим , [18] что по-прежнему имело место в отчете за 2022 год. [19] 19 марта 2019 года Назарбаев объявил о своей отставке с поста президента. [53] Спикер сената Казахстана Касым-Жомарт Токаев победил на президентских выборах 2019 года , которые состоялись 9 июня. [54] [55] Его первым официальным актом стало переименование столицы в честь своего предшественника. [56] В январе 2022 года страна погрузилась в политические беспорядки из-за скачка цен на топливо. [57] В результате президент Касым-Жомарт Токаев занял пост главы могущественного Совета безопасности, отстранив своего предшественника Нурсултана Назарбаева от должности. [58] В сентябре 2022 года название столицы страны было изменено с Нур-Султана на Астану. [59]

Поскольку Казахстан простирается по обоим берегам реки Урал , считающейся разделительной линией между Европой и Азией, он является одной из двух стран в мире, не имеющих выхода к морю, территория которой расположена на двух континентах (вторая — Азербайджан ).
С площадью 2 700 000 квадратных километров (1 000 000 квадратных миль) — эквивалентной по размеру Западной Европе — Казахстан является девятой по величине страной и крупнейшей страной в мире, не имеющей выхода к морю. Будучи частью Российской империи , Казахстан потерял часть своей территории в пользу китайской провинции Синьцзян [60] , а часть — в пользу автономной республики Узбекистан Каракалпакстан в советские годы.

Он имеет общую границу с Россией протяженностью 6846 километров (4254 миль), с Узбекистаном — 2203 километра (1369 миль), с Китаем — 1533 километра (953 мили), с Кыргызстаном — 1051 километр (653 мили ) и с Туркменистаном — 379 километров (235 миль) . Крупнейшие города включают Астану , Алматы , Караганду , Шымкент , Атырау и Усть-Каменогорск . Он расположен между широтами 40° и 56° с. ш . и долготами 46° и 88° в. д . Хотя Казахстан расположен в основном в Азии, небольшая часть его также расположена к западу от Урала в Восточной Европе. [61]
Рельеф Казахстана простирается с запада на восток от Каспийского моря до Алтайских гор и с севера на юг от равнин Западной Сибири до оазисов и пустынь Центральной Азии. Казахская степь (равнина) площадью около 804 500 квадратных километров (310 600 квадратных миль) занимает треть страны и является крупнейшим в мире регионом сухой степи . Степь характеризуется большими площадями лугов и песчаных районов. Основные моря, озера и реки включают озеро Балхаш , озеро Зайсан , реку Чарын и ущелье , реки Или , Иртыш , Ишим , Урал и Сырдарья , а также Аральское море , пока оно в значительной степени не высохло в результате одной из самых страшных экологических катастроф в мире. [62]

Чарынский каньон имеет длину 80 километров (50 миль), прорезая плато красного песчаника и тянется вдоль ущелья реки Чарын в северном Тянь-Шане («Небесные горы», 200 км (124 мили) к востоку от Алматы) на 43°21′1.16″ с. ш. 79°4′49.28″ в. д. / 43.3503222° с. ш. 79.0803556° в. д. / 43.3503222; 79.0803556 . Крутые склоны каньона, колонны и арки поднимаются на высоту от 150 до 300 метров (490 и 980 футов). Недоступность каньона обеспечила безопасное убежище для редкого ясеня Fraxinus sogdiana , который пережил там ледниковый период и теперь также растет в некоторых других районах. [63] Кратер Бигач , на 48°30′ с. ш. 82°00′ в. д. / 48.500° с. ш. 82.000° в. д. / 48.500; 82.000 , представляет собой плиоценовый или миоценовый астероидный кратер диаметром 8 км (5 миль), возраст которого оценивается в 5±3 миллиона лет.
В Алматинской области Казахстана также находится горное плато Мынжылкы .

Казахстан обладает обильными запасами доступных минеральных и ископаемых топливных ресурсов. Разработка нефти, природного газа и добыча полезных ископаемых привлекла большую часть из более чем 40 миллиардов долларов иностранных инвестиций в Казахстан с 1993 года и составляет около 57 процентов промышленного производства страны (или примерно 13 процентов валового внутреннего продукта). По некоторым оценкам, [64] Казахстан имеет вторые по величине запасы урана , хрома , свинца и цинка ; третьи по величине запасы марганца ; пятые по величине запасы меди; и входит в десятку лучших по углю, железу и золоту. Он также является экспортером алмазов. Возможно, наиболее значимым для экономического развития является то, что Казахстан также имеет 11-е по величине доказанные запасы как нефти, так и природного газа. [65] Одним из таких мест является Токаревское газоконденсатное месторождение .
Всего насчитывается 160 месторождений с более чем 2,7 млрд тонн (2,7 млрд длинных тонн) нефти. Разведка нефти показала, что месторождения на побережье Каспия являются лишь малой частью гораздо более крупного месторождения. Говорят, что в этой области можно найти 3,5 млрд тонн (3,4 млрд длинных тонн) нефти и 2,5 млрд кубометров (88 млрд кубических футов) газа. Общая оценка нефтяных месторождений Казахстана составляет 6,1 млрд тонн (6,0 млрд длинных тонн). Однако в стране есть только три нефтеперерабатывающих завода , расположенных в Атырау , [66] Павлодаре и Шымкенте . Они не способны перерабатывать весь объем сырой нефти, поэтому большая ее часть экспортируется в Россию. По данным Управления энергетической информации США , в 2009 году Казахстан добывал приблизительно 1 540 000 баррелей (245 000 м 3 ) нефти в день. [67]
Казахстан также обладает крупными месторождениями фосфорита . Два крупнейших месторождения включают бассейн Каратау с 650 миллионами тонн P2O5 и месторождение Чилисай Актюбинского фосфоритового бассейна, расположенного на северо-западе Казахстана, с ресурсами 500–800 миллионов тонн 9-процентной руды. [68] [ 69]
17 октября 2013 года Инициатива прозрачности в добывающих отраслях (ИПДО) признала Казахстан «соответствующим ИПДО», что означает, что в стране действует базовый и функциональный процесс, обеспечивающий регулярное раскрытие доходов от природных ресурсов. [70]

Казахстан имеет «экстремальный» континентальный и холодный степной климат и прочно сидит внутри евразийской степи , включая казахскую степь , с жарким летом и очень холодной зимой. Действительно, Астана является второй самой холодной столицей в мире после Улан-Батора . Осадки варьируются между засушливыми и полузасушливыми условиями, зима особенно сухая. [71]

В Казахстане есть десять природных заповедников и десять национальных парков , которые обеспечивают безопасное убежище для многих редких и находящихся под угрозой исчезновения растений и животных. Всего существует двадцать пять территорий охраны . Распространенными растениями являются Astragalus , Gagea , Allium , Carex и Oxytropis ; к исчезающим видам растений относятся местная дикая яблоня ( Malus sieversii ), дикий виноград ( Vitis vinifera ) и несколько видов диких тюльпанов (например, Tulipa greigii ) и редкие виды лука Allium karataviense , а также Iris willmottiana и Tulipa kaufmanniana . [73] [74] Средний балл Индекса целостности лесных ландшафтов Казахстана за 2019 год составил 8,23/10, что поставило его на 26-е место в мире из 172 стран. [75]
Распространенные млекопитающие включают волка , лисицу , корсака , лося , архара (крупнейший вид овец), рысь , кота Палласа и снежного барса , некоторые из которых находятся под защитой. В Красной книге охраняемых видов Казахстана перечислены 125 позвоночных, включая множество птиц и млекопитающих, и 404 растения, включая грибы, водоросли и лишайники. [76]
Лошадь Пржевальского была вновь завезена в степи спустя почти 200 лет. [77]
Официально Казахстан является демократической, светской, конституционной унитарной республикой ; Нурсултан Назарбаев руководил страной с 1991 по 2019 год. [78] [79] Его преемником стал Касым-Жомарт Токаев . [80] [81] Президент может наложить вето на законы, принятые парламентом , а также является главнокомандующим вооруженными силами . Премьер-министр возглавляет кабинет министров и является главой правительства Казахстана. В кабинете министров три заместителя премьер-министра и шестнадцать министров. [82]
В Казахстане двухпалатный парламент, состоящий из Мажилиса ( нижняя палата ) и Сената ( верхняя палата ). [83] Одномандатные округа всенародно избирают 107 мест в Мажилисе ; также есть десять членов, избираемых по партийным спискам. Сенат состоит из 48 членов. Два сенатора избираются каждым из выборных собраний ( мяслихатов ) шестнадцати основных административных единиц Казахстана (четырнадцать областей плюс города Астана, Алматы и Шымкент). Президент назначает оставшихся пятнадцать сенаторов. Депутаты Мажилиса и правительство имеют право законодательной инициативы, хотя правительство предлагает большую часть законопроектов, рассматриваемых парламентом. В 2020 году Freedom House оценил Казахстан как «консолидированный авторитарный режим», заявив, что свобода слова не соблюдается и «избирательное законодательство Казахстана не обеспечивает свободных и справедливых выборов ». [84]
Реформы начали осуществляться после избрания Касым-Жомарта Токаева в июне 2019 года. Токаев поддерживает культуру оппозиции, публичных собраний и смягчения правил формирования политических партий. [85] В июне 2019 года Токаев создал Национальный совет общественного доверия в качестве общественной платформы для общенационального диалога относительно государственной политики и реформ. [86] В июле 2019 года президент Казахстана объявил о концепции «слушающего государства», которое быстро и эффективно реагирует на все конструктивные запросы граждан страны. [87] Будет принят закон, позволяющий представителям других партий занимать должности председателей в некоторых парламентских комитетах, чтобы способствовать формированию альтернативных взглядов и мнений. [ когда? ] Минимальный порог членства, необходимый для регистрации политической партии, будет снижен с 40 000 до 20 000 членов. [86] Будут выделены специальные места для мирных митингов в центральных районах, а также будет принят новый законопроект, определяющий права и обязанности организаторов, участников и наблюдателей. [86] В целях повышения общественной безопасности президент Токаев ужесточил наказания для лиц, совершающих преступления против личности. [86]
17 сентября 2022 года Токаев подписал указ, ограничивающий срок полномочий президента одним семилетним сроком. [88] Кроме того, он объявил о подготовке нового пакета реформ по «децентрализации» и «распределению» власти между государственными учреждениями. Пакет реформ также направлен на изменение избирательной системы и расширение полномочий по принятию решений в регионах Казахстана. [89] Полномочия парламента были расширены за счет полномочий президента, родственникам которого теперь также запрещено занимать государственные должности, в то время как Конституционный суд был восстановлен, а смертная казнь отменена. [89] [90]
Казахстан разделен на семнадцать регионов ( казахский : облыстар , oblystar ; русский : области , regions ) плюс три города (Алматы, Астана и Шымкент), которые независимы от региона, в котором они расположены. Регионы подразделяются на 177 районов ( казахский : аудандар , audandar ; русский : районы , rayony ). [91] Районы далее подразделяются на сельские районы на самом низком уровне администрации, которые включают все сельские поселения и деревни без связанного с ними муниципального управления. [92]
Города Алматы и Астана имеют статус «государственного значения» и не относятся ни к одному региону. Город Байконур имеет особый статус, поскольку он сдается в аренду до 2050 года России для космодрома Байконур . [93] В июне 2018 года город Шымкент стал «городом республиканского значения». [94]
Каждый регион возглавляет аким (губернатор области), назначаемый президентом. Районные акимы назначаются областными акимами . Правительство Казахстана перенесло свою столицу из Алматы, созданной во времена Советского Союза, в Астану 10 декабря 1997 года. [95]
Municipalities exist at each level of administrative division in Kazakhstan. Cities of republican, regional, and district significance are designated as urban inhabited localities; all others are designated rural.[92] At the highest level are the cities of Almaty and Astana, which are classified as cities of republican significance on the administrative level equal to that of a region.[91] At the intermediate level are cities of regional significance on the administrative level equal to that of a district. Cities of these two levels may be divided into city districts.[91] At the lowest level are cities of district significance, and over two-thousand villages and rural settlements (aul) on the administrative level equal to that of rural districts.[91]

Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Economic Cooperation Organization and the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. The nations of Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan established the Eurasian Economic Community in 2000, to revive earlier efforts to harmonise trade tariffs and to create a free trade zone under a customs union. On 1 December 2007, it was announced that Kazakhstan had been chosen to chair the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe for the year 2010. Kazakhstan was elected a member of the UN Human Rights Council for the first time on 12 November 2012.[97]
Kazakhstan is also a member of the United Nations, Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council, Turkic Council, and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC). It is an active participant in the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation Partnership for Peace program.[98]
In 1999, Kazakhstan had applied for observer status at the Council of Europe Parliamentary Assembly. The official response of the Assembly was that because Kazakhstan is partially located in Europe,[99][100] it could apply for full membership, but that it would not be granted any status whatsoever at the council until its democracy and human rights records improved.
Since independence in 1991, Kazakhstan has pursued what is known as the "multi-vector foreign policy" (Kazakh: көпвекторлы сыртқы саясат), seeking equally good relations with its two large neighbours, Russia and China, as well as with the United States and the rest of the Western world.[101][102] Russia leases approximately 6,000 square kilometres (2,317 sq mi) of territory enclosing the Baikonur Cosmodrome space launch site in south central Kazakhstan, where the first man was launched into space as well as Soviet space shuttle Buran and the well-known space station Mir.
On 11 April 2010, presidents Nazarbayev and Obama met at the Nuclear Security Summit in Washington, D.C., and discussed strengthening the strategic partnership between the United States and Kazakhstan. They pledged to intensify bilateral co-operation to promote nuclear safety and non-proliferation, regional stability in Central Asia, economic prosperity, and universal values.[103]
Since 2014, the Kazakhstani government has been bidding for a non-permanent member seat on the UN Security Council for 2017–2018.[104] On 28 June 2016 Kazakhstan was elected as a non-permanent member to serve on the UN Security Council for a two-year term.[105]

Kazakhstan has supported UN peacekeeping missions in Haiti, Western Sahara, and Côte d'Ivoire.[106] In March 2014, the Ministry of Defense chose 20 Kazakhstani military men as observers for the UN peacekeeping missions. The military personnel, ranking from captain to colonel, had to go through specialised UN training; they had to be fluent in English and skilled in using specialised military vehicles.[106]
In 2014, Kazakhstan gave Ukraine humanitarian aid during the conflict with Russian-backed rebels. In October 2014, Kazakhstan donated $30,000 to the International Committee of the Red Cross's humanitarian effort in Ukraine. In January 2015, to help the humanitarian crisis, Kazakhstan sent $400,000 of aid to Ukraine's southeastern regions.[107] President Nazarbayev said of the war in Ukraine, "The fratricidal war has brought true devastation to eastern Ukraine, and it is a common task to stop the war there, strengthen Ukraine's independence and secure territorial integrity of Ukraine."[108] Experts believe that no matter how the Ukraine crisis develops, Kazakhstan's relations with the European Union will remain normal.[109] It is believed that Nazarbayev's mediation is positively received by both Russia and Ukraine.[109]
Kazakhstan's Ministry of Foreign Affairs released a statement on 26 January 2015: "We are firmly convinced that there is no alternative to peace negotiations as a way to resolve the crisis in south-eastern Ukraine."[110] In 2018, Kazakhstan signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.[111]
_01.jpg/440px-Putin-Tokayev_meeting_(2022-11-28)_01.jpg)
On 6 March 2020, the Concept of the Foreign Policy of Kazakhstan for 2020–2030 was announced. The document outlines the following main points:
Kazakhstan's memberships of international organisations include:
Based on these principles, following Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, Kazakhstan has increasingly pursued an independent foreign policy, defined by its own foreign policy objectives and ambitions[116][117] through which the country attempts to balance its relations with "all the major powers and an equally principled aversion towards excessive dependence in any field upon any one of them, while also opening the country up economically to all who are willing to invest there."[118]
Kazakhstan is the 59th most peaceful country in the world, according to the 2024 Global Peace Index.[119]
.jpg/440px-A_Kazakh_Sukhoi_Su-27P(modified).jpg)
Most of Kazakhstan's military was inherited from the Soviet Armed Forces' Turkestan Military District. These units became the core of Kazakhstan's new military. It acquired all the units of the 40th Army (the former 32nd Army) and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land-force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments, and a large amount of equipment that had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. Since the late 20th century, the Kazakhstan Army has focused on expanding the number of its armoured units. Since 1990, armoured units have expanded from 500 to 1,613 in 2005.
The Kazakh air force is composed mostly of Soviet-era planes, including 41 MiG-29s, 44 MiG-31s, 37 Su-24s and 60 Su-27s. A small naval force is maintained on the Caspian Sea.[120]
Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq to assist the US post-invasion mission in Iraq.[121] During the second Iraq War, Kazakhstani troops dismantled 4 million mines and other explosives, helped provide medical care to more than 5,000 coalition members and civilians, and purified 718 cubic metres (25,400 cu ft) of water.[122]
Kazakhstan's National Security Committee (UQK) was established on 13 June 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, Border Guard, several Commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau). The latter is considered the most important part of KNB. Its director is Nurtai Abykayev.
Since 2002, the joint tactical peacekeeping exercise "Steppe Eagle" has been hosted by the Kazakhstan government. "Steppe Eagle" focuses on building coalitions and gives participating nations the opportunity to work together. During the Steppe Eagle exercises, the KAZBAT peacekeeping battalion operates within a multinational force under a unified command within multidisciplinary peacekeeping operations, with NATO and the U.S. Military.[123]
In December 2013, Kazakhstan announced it will send officers to support United Nations Peacekeeping forces in Haiti, Western Sahara, Ivory Coast and Liberia.[124]
The Economist Intelligence Unit has consistently ranked Kazakhstan as an "authoritarian regime" in its Democracy Index, ranking it 128th out of 167 countries for 2020.[125][126]
Kazakhstan was ranked 122nd out of 180 countries in Reporters Without Borders' Press Freedom Index for 2022; previously it ranked 155th for 2021.[127]
Kazakhstan's human rights situation has been described as poor by independent observers. In its 2015 report of human rights in the country, Human Rights Watch said that "Kazakhstan heavily restricts freedom of assembly, speech, and religion."[128] It has also described the government as authoritarian.[129] In 2014, authorities closed newspapers, jailed or fined dozens of people after peaceful but unsanctioned protests, and fined or detained worshipers for practising religion outside state controls. Government critics, including opposition leader Vladimir Kozlov, remained in detention after unfair trials. In mid-2014, Kazakhstan adopted new criminal, criminal executive, criminal procedural, and administrative codes, and a new law on trade unions, which contain articles restricting fundamental freedoms and are incompatible with international standards. Torture remains common in places of detention."[130] However, Kazakhstan has achieved significant progress in reducing the prison population.[131] The 2016 Human Rights Watch report commented that Kazakhstan "took few meaningful steps to tackle a worsening human rights record in 2015, maintaining a focus on economic development over political reform."[132] Some critics of the government have been arrested for allegedly spreading false information about the COVID-19 pandemic in Kazakhstan.[133] Various police reforms, like creation of local police service and zero-tolerance policing, aimed at bringing police closer to local communities have not improved cooperation between police and ordinary citizens.[134]
According to a U.S. government report released in 2014, in Kazakhstan:
The law does not require police to inform detainees that they have the right to an attorney, and police did not do so. Human rights observers alleged that law enforcement officials dissuaded detainees from seeing an attorney, gathered evidence through preliminary questioning before a detainee's attorney arrived, and in some cases used corrupt defense attorneys to gather evidence. [...][135]
The law does not adequately provide for an independent judiciary. The executive branch sharply limited judicial independence. Prosecutors enjoyed a quasi-judicial role and had the authority to suspend court decisions. Corruption was evident at every stage of the judicial process. Although judges were among the most highly paid government employees, lawyers and human rights monitors alleged that judges, prosecutors, and other officials solicited bribes in exchange for favorable rulings in the majority of criminal cases.[135]
Kazakhstan's global rank in the World Justice Project's 2015 Rule of Law Index was 65 out of 102; the country scored well on "Order and Security" (global rank 32/102), and poorly on "Constraints on Government Powers" (global rank 93/102), "Open Government" (85/102) and "Fundamental Rights" (84/102, with a downward trend marking a deterioration in conditions).[136]
The ABA Rule of Law Initiative of the American Bar Association has programs to train justice sector professionals in Kazakhstan.[137][138]
Kazakhstan's Supreme Court has taken steps to modernise and to increase transparency and oversight over the country's legal system. With funding from the US Agency for International Development, the ABA Rule of Law Initiative began a new program in April 2012 to strengthen the independence and accountability of Kazakhstan's judiciary.[139]
In an effort to increase transparency in the criminal justice and court system, and improve human rights, Kazakhstan intended to digitise all investigative, prosecutorial and court records by 2018.[140] Many criminal cases are closed before trial on the basis of reconciliation between the defendant and the victim because they simplify the work of the law-enforcement officers, release the defendant from punishment, and pay little regard to the victim's rights.[141]
Homosexuality has been legal in Kazakhstan since 1997, although it is still socially unacceptable in most areas.[142] Discrimination against LGBT people in Kazakhstan is widespread.[143][144]

In 2018, Kazakhstan had a GDP of $179.332 billion and an annual growth rate of 4.5 percent. Per capita, Kazakhstan's GDP stood at $9,686.[145] Buoyed by high world crude oil prices, GDP growth figures were between 8.9 percent and 13.5 percent from 2000 to 2007 before decreasing to 1 to 3 percent in 2008 and 2009, and then rising again from 2010.[146] Other major exports of Kazakhstan include wheat, textiles, and livestock. Kazakhstan is a leading exporter of uranium.[147][148]
Kazakhstan's economy grew by 4.6 percent in 2014.[149] The country experienced a slowdown in economic growth from 2014 sparked by falling oil prices and the effects of the Ukrainian crisis.[150] The country devalued its currency by 19 percent in February 2014.[151] Another 22 percent devaluation occurred in August 2015.[152] Kazakhstan was the first former Soviet Republic to repay all of its debt to the International Monetary Fund, 7 years ahead of schedule.[153]
Kazakhstan weathered the global financial crisis [citation needed] by combining fiscal relaxation with monetary stabilisation. In 2009, the government introduced large-scale support measures such as the recapitalisation of banks and support for the real estate and agricultural sectors, as well as for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). The total value of the stimulus programs amounted to $21 billion, or 20 per cent of the country's GDP, with $4 billion going to stabilise the financial sector.[154] During the global economic crisis, Kazakhstan's economy contracted by 1.2 percent in 2009, while the annual growth rate subsequently increased to 7.5 percent and 5 percent in 2011 and 2012, respectively.[155] Kazakhstan's government continued to follow a conservative fiscal policy by controlling budget spending and accumulating oil revenue savings in its Oil Fund – Samruk-Kazyna. The global financial crisis forced Kazakhstan to increase its public borrowing to support the economy. Public debt increased to 13.4 per cent in 2013 from 8.7 per cent in 2008. Between 2012 and 2013, the government achieved an overall fiscal surplus of 4.5 per cent.[156]
In March 2002, the U.S. Department of Commerce granted Kazakhstan market economy status under US trade law. This change in status recognised substantive market economy reforms in the areas of currency convertibility, wage rate determination, openness to foreign investment, and government control over the means of production and allocation of resources. In September 2002, Kazakhstan became the first country in the CIS to receive an investment grade credit rating from a major international credit rating agency.[157] By late December 2003, Kazakhstan's gross foreign debt was about $22.9 billion. Total governmental debt was $4.2 billion, 14 percent of GDP. There has been a reduction in the ratio of debt to GDP. The ratio of total governmental debt to GDP was 21.7 percent in 2000, 17.5 percent in 2001, and 15.4 percent in 2002. In 2019, it rose to 19.2 percent.[158]

On 29 November 2003, the Law on Changes to Tax Code which reduced tax rates was adopted. The value added tax fell from 16% to 15%, the social tax, payable by all employers, from 21 percent to 20 percent, and the personal income tax from 30 percent to 20 percent. On 7 July 2006, the personal income tax was reduced even further to a flat rate of 5 percent for personal income in the form of dividends and 10 percent for other personal income. Kazakhstan furthered its reforms by adopting a new land code on 20 June 2003, and a new customs code on 5 April 2003.
Kazakhstan instituted a pension reform program in 1998. By January 2012, the pension assets were about $17 billion (KZT 2.5 trillion). There are 11 saving pension funds in the country. The State Accumulating Pension Fund, the only state-owned fund, was privatised in 2006. The country's unified financial regulatory agency oversees and regulates pension funds. The growing demand of pension funds for investment outlets triggered the development of the debt securities market. Pension fund capital is being invested almost exclusively in corporate and government bonds, including the government of Kazakhstan Eurobonds. The government of Kazakhstan was studying a project to create a unified national pension fund and transfer all the accounts from the private pension funds into it.[159]
Kazakhstan climbed to 41st on the 2018 Economic Freedom Index published by The Wall Street Journal and The Heritage Foundation.[160]
Kazakhstan's increased role in global trade and central positioning on the new Silk Road gave the country the potential to open its markets to billions of people.[161] Kazakhstan joined the World Trade Organization in 2015.[162]
Kazakhstan's foreign trade turnover in 2018 was $93.5 billion, which is 19.7 percent more than in 2017. Export in 2018 reached $67 billion (up 25.7 percent in comparison to 2017) and import was $32.5 billion (up 9.9 percent in comparison to 2017).[163] Exports accounted for 40.1 percent of Kazakhstan's gross domestic product (GDP) in 2018. Kazakhstan exports 800 products to 120 countries.[164]
.jpg/440px-Песня_жаворонка(3264-2448).jpg)
Agriculture accounts for approximately 5 percent of Kazakhstan's GDP.[93] Grain, potatoes, grapes, vegetables, melons and livestock are the most important agricultural commodities. Agricultural land occupies more than 846,000 square kilometres (327,000 sq mi). The available agricultural land consists of 205,000 km2 (79,000 sq mi) of arable land and 611,000 km2 (236,000 sq mi) of pasture and hay land. Over 80 percent of the country's total area is classified as agricultural land, including almost 70 percent occupied by pasture. Its arable land has the second highest availability per inhabitant (1.5 hectares).[165]
Chief livestock products are dairy products, leather, meat, and wool. The country's major crops include wheat, barley, cotton, and rice. Wheat exports, a major source of hard currency, rank among the leading commodities in Kazakhstan's export trade. In 2003 Kazakhstan harvested 17.6 million tons of grain in gross, 2.8% higher compared to 2002. Kazakhstani agriculture still has many environmental problems from mismanagement during its years in the Soviet Union. Some Kazakh wine is produced in the mountains to the east of Almaty.[166]
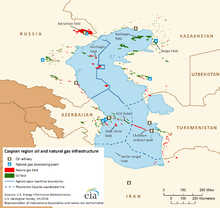
Energy has been the leading economic sector. Production of crude oil and natural gas condensate from the oil and gas basins of Kazakhstan amounted to 79.2 million tonnes (77.9 million long tons; 87.3 million short tons) in 2012 up from 51.2 million tonnes (50.4 million long tons; 56.4 million short tons) in 2003. Kazakhstan raised oil and gas condensate exports to 44.3 million tons in 2003, 13 percent higher than in 2002. Gas production in Kazakhstan in 2003, amounted to 13.9 billion cubic metres (490 billion cubic feet), up 22.7 percent compared to 2002, including natural gas production of 7.3 billion cubic metres (260 billion cubic feet). Kazakhstan holds about 4 billion tonnes (3.9 billion long tons; 4.4 billion short tons) of proven recoverable oil reserves and 2,000 cubic kilometres (480 cubic miles) of gas. Kazakhstan is the 19th largest oil-producing nation in the world.[167] Kazakhstan's oil exports in 2003, were valued at more than $7 billion, representing 65 percent of overall exports and 24 percent of the GDP. Major oil and gas fields and recoverable oil reserves are Tengiz with 7 billion barrels (1.1 billion cubic metres); Karachaganak with 8 billion barrels (1.3 billion cubic metres) and 1,350 cubic kilometres (320 cubic miles) of natural gas; and Kashagan with 7 to 9 billion barrels (1.4 billion cubic metres).
KazMunayGas (KMG), the national oil and gas company, was created in 2002 to represent the interests of the state in the oil and gas industry. The Tengiz Field was jointly developed in 1993 as a 40-year Tengizchevroil venture between Chevron Texaco (50 percent), US ExxonMobil (25 percent), KazMunayGas (20 percent), and LukArco (5 percent).[168] The Karachaganak natural gas and gas condensate field is being developed by BG, Agip, ChevronTexaco, and Lukoil.[169] Also Chinese oil companies are involved in Kazakhstan's oil industry.[170]
Kazakhstan launched the Green Economy Plan in 2013. It committed Kazakhstan to meet 50 percent of its energy needs from alternative and renewable sources by 2050.[171] The green economy was projected to increase GDP by 3 percent and create some 500,000 jobs.[172] The government set prices for energy produced from renewable sources. The price of 1 kilowatt-hour for energy produced by wind power plants was set at 22.68 tenge ($0.12), for 1 kilowatt-hour produced by small hydro-power plants 16.71 tenges ($0.09), and from biogas plants 32.23 tenges ($0.18).[173]


Railways provide 68 percent of all cargo and passenger traffic to over 57 percent of the country. There are 15,333 km (9,527 mi) in common carrier service, excluding industrial lines.[174]15,333 km (9,527 mi) of 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) gauge, 4,000 km (2,500 mi) electrified, in 2012.[174] Most cities are connected by railroad; high-speed trains go from Almaty (the southernmost city) to Petropavl (the northernmost city) in about 18 hours.
Kazakhstan Temir Zholy (KTZ) is the national railway company. KTZ cooperates with French locomotive manufacturer Alstom in developing Kazakhstan's railway infrastructure. As of 2018, Alstom has more than 600 staff and two joint ventures with KTZ and its subsidiary in Kazakhstan.[175] In July 2017, Alstom opened its first locomotive repairing centre in Kazakhstan. It is the only repairing centre in Central Asia and the Caucasus.[176] Astana Nurly Zhol railway station, the most modern railway station in Kazakhstan, was opened in Astana on 31 May 2017. According to Kazakhstan Railways (KTZ), the 120,000m2 station was expected to be used by 54 trains and would have the capacity to handle 35,000 passengers a day.[177]
There is a small 8.56 km (5.32 mi) metro system in Almaty. Second and third metro lines were planned for the future. The second line would intersect with the first line at Alatau and Zhibek Zholy stations.[178] The Astana Metro system has been under construction, but was abandoned at one point in 2013.[179] In May 2015, an agreement was signed for the project to be resumed.[180] There is an 86 km (53 mi) tram network, which began service in 1965 with, as of 2012, 20 regular and three special routes.[181]
The Khorgos Gateway dry port is one of Kazakhstan's primary dry ports for handling trans-Eurasian trains, which travel more than 9,000 km (5,600 mi) between China and Europe. The Khorgos Gateway dry port is surrounded by Khorgos Eastern Gate SEZ which officially commenced operations in December 2016.[182]
In 2009, the European Commission blacklisted all Kazakh air carriers with a sole exception of Air Astana.[183] Thereafter, Kazakhstan took measures to modernise and revamp its air safety oversight. In 2016 the European air safety authorities removed all Kazakh airlines from the blacklist, saying there was "sufficient evidence of compliance" with international standards by Kazakh Airlines and the Civil Aviation Committee.[184]


Kazakhstan is the ninth-largest country by area and the largest landlocked country in the world. As of 2014, tourism accounted for 0.3 percent of Kazakhstan's GDP, but the government had plans to increase it to 3 percent by 2020.[185][186] According to the World Economic Forum's Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report of 2017, travel and tourism industry GDP in Kazakhstan was $3.08 billion or only 1.6 percent of total GDP. The WEF ranked Kazakhstan 80th in its 2019 report.[187]
In 2017, Kazakhstan ranked 43rd in the number of tourist arrivals. In 2014, The Guardian described tourism in Kazakhstan as "hugely underdeveloped", despite the country's mountain, lake and desert landscapes.[188] Factors hampering an increase in tourism were said to include high prices, "shabby infrastructure", "poor service" and the difficulties of travel in a large underdeveloped country.[188] Even for Kazakhs, going for a holiday abroad may cost only half the price of taking a holiday in Kazakhstan.[188]
The Kazakh Government, long characterised as authoritarian with a history of human rights abuses and suppression of political opposition,[16] in 2015 issued a "Tourism Industry Development Plan 2020." It aimed to establish five tourism clusters in Kazakhstan: Astana city, Almaty city, East Kazakhstan, South Kazakhstan, and West Kazakhstan Oblasts. It also sought investment of $4 billion and the creation of 300,000 new jobs in the tourism industry by 2020.[189][188]
Kazakhstan has offered a permanent visa-free regime for up to 90 days to citizens of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Russia and Ukraine, and for up to 30 days to citizens of Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador, Serbia, South Korea, Tajikistan, Turkey, UAE and Uzbekistan. It also established a visa-free regime for citizens of 54 countries, including the European Union and OECD member states, the U.S., Japan, Mexico, Australia and New Zealand.[190][191]
Kazakhstan has attracted $330 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI) from more than 120 countries since its independence (1991).[192] In 2015, the U.S. State Department said Kazakhstan was widely considered to have the best investment climate in the region.[193] In 2014, President Nazarbayev signed into law tax concessions to promote foreign direct investment which included a 10-year exemption from corporation tax, an eight-year exemption from property tax, and a 10-year freeze on most other taxes.[194] Other incentives include a refund on capital investments of up to 30 percent once a production facility is in operation.[194]In 2012, Kazakhstan attracted $14 billion of foreign direct investment inflows into the country at a 7 percent growth rate.[195] In 2018, $24 billion of FDI was directed into Kazakhstan, a significant increase since 2012.[196]
In 2014, the European Bank of Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and Kazakhstan created the partnership for Re-Energizing the Reform Process in Kazakhstan to work with international financial institutions to channel US$2.7 billion provided by the Kazakh government into important sectors of Kazakhstan's economy.[197]As of May 2014, Kazakhstan had attracted $190 billion in gross foreign investments since its independence in 1991 and it led the CIS countries in terms of FDI attracted per capita.[198] The OECD 2017 Investment Policy Review noted that "great strides" had been made to open up opportunities to foreign investors and improve policy to attract FDI.[199]China is one of the main economic and trade partners of Kazakhstan. In 2013, China launched the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in which Kazakhstan functions as a transit hub.[200]
The banking industry of Kazakhstan went through a boom-and-bust cycle in the early 21st century. After several years of rapid expansion in the mid-2000s, the banking industry collapsed in 2008. Several large banking groups, including BTA Bank J.S.C. and Alliance Bank, defaulted soon thereafter. The industry shrank and was restructured, with system-wide loans dropping from 59 percent of GDP in 2007 to 39 percent in 2011. The Kazakh National Bank introduced deposit insurance in a campaign to strengthen the banking sector. Several major foreign banks had branches in Kazakhstan, including RBS, Citibank, and HSBC. Kookmin and UniCredit both entered Kazakhstan's financial services market through acquisitions and stake-building. [citation needed]
According to the 2010–11 World Economic Forum in Global Competitiveness Report, Kazakhstan was ranked 72nd in the world in economic competitiveness.[201] One year later, the Global Competitiveness Report ranked Kazakhstan 50th in most competitive markets.[202]
In the 2020 Doing Business Report by the World Bank, Kazakhstan ranked 25th globally and as the number one best country globally for protecting minority investors' rights.[203] Kazakhstan achieved its goal of entering the top 50 most competitive countries in 2013 and has maintained its position in the 2014–2015 World Economic Forum Global Competitiveness Report that was published at the beginning of September 2014.[204] Kazakhstan is ahead of other states in the CIS in almost all of the report's pillars of competitiveness, including institutions, infrastructure, macroeconomic environment, higher education and training, goods market efficiency, labour market development, financial market development, technological readiness, market size, business sophistication and innovation, lagging behind only in the category of health and primary education.[204] The Global Competitiveness Index gives a score from 1 to 7 in each of these pillars, and Kazakhstan earned an overall score of 4.4.[204]
In 2005, the World Bank listed Kazakhstan as a corruption hotspot, on a par with Angola, Bolivia, Kenya, Libya and Pakistan.[205] In 2012, Kazakhstan ranked low in an index of the least corrupt countries[206] and the World Economic Forum listed corruption as the biggest problem in doing business in the country.[206] A 2017 OECD report on Kazakhstan indicated that Kazakhstan has reformed laws with regard to the civil service, judiciary, instruments to prevent corruption, access to information, and prosecuting corruption.[207] Kazakhstan has implemented anticorruption reforms that have been recognised by organizations like Transparency International.[208]
In 2011, Switzerland confiscated US$48 million in Kazakhstani assets from Swiss bank accounts, as a result of a bribery investigation in the United States.[209] US officials believed the funds represented bribes paid by American officials to Kazakhstani officials in exchange for oil or prospecting rights in Kazakhstan. Proceedings eventually involved US$84 million in the US and another US$60 million in Switzerland.[209]
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Kazakh Anti-Corruption Agency signed a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty in February 2015.[210]
Transparency International's 2023 Corruption Perceptions Index, which scored 180 countries on a scale from 0 ("highly corrupt") to 100 ("very clean"), gave Kazakhstan a score of 39. When ranked by score, Kazakhstan ranked 93rd among the 180 countries in the Index, where the country ranked first is perceived to have the most honest public sector.[211] For comparison with worldwide scores, the best score was 90 (ranked 1), the average score was 43, and the worst score was 11 (ranked 180).[212] For comparison with regional scores, the highest score among Eastern European and Central Asian countries [e] was 53, the average score was 35 and the lowest score was 18.[213]

Research remains largely concentrated in Kazakhstan's largest city and former capital, Almaty, home to 52 percent of research personnel. Public research is largely confined to institutes, with universities making only a token contribution. Research institutes receive their funding from national research councils under the umbrella of the Ministry of Education and Science. Their output, however, tends to be disconnected from market needs. In the business sector, few industrial enterprises conduct research themselves.[214][215]

One of the most ambitious targets of the State Programme for Accelerated Industrial and Innovative Development adopted in 2010 is to raise the country's level of expenditure on research and development to 1 percent of GDP by 2015. By 2013, this ratio stood at 0.18 percent of GDP. It will be difficult to reach the target as long as economic growth remains strong.[needs update] Since 2005, the economy has grown faster (by 6 percent in 2013) than gross domestic expenditure on research and development, which only progressed from PPP$598 million to PPP$714 million between 2005 and 2013.[215]
Innovation expenditure more than doubled in Kazakhstan between 2010 and 2011, representing KZT 235 billion (circa US$1.6 billion), or around 1.1 percent of GDP. Some 11 percent of the total was spent on research and development. This compares with about 40 to 70 percent of innovation expenditure in developed countries. This augmentation was due to a sharp rise in product design and the introduction of new services and production methods over this period, to the detriment of the acquisition of machinery and equipment, which has traditionally made up the bulk of Kazakhstan's innovation expenditure. Training costs represented just 2 percent of innovation expenditure, a much lower share than in developed countries.[214][215] Kazakhstan was ranked 81st in the Global Innovation Index in 2023.[216]
In December 2012, President Nursultan Nazarbayev announced the Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy with the slogan "Strong Business, Strong State." This pragmatic strategy proposes sweeping socio-economic and political reforms to hoist Kazakhstan among the top 30 economies by 2050. In this document, Kazakhstan gives itself 15 years to evolve into a knowledge economy. New sectors are to be created during each five-year plan. The first of these, covering the years 2010–2014, focused on developing industrial capacity in car manufacturing, aircraft engineering and the production of locomotives, passenger and cargo railroad cars. During the second five-year plan to 2019, the goal is to develop export markets for these products. To enable Kazakhstan to enter the world market of geological exploration, the country intends to increase the efficiency of traditional extractive sectors such as oil and gas. It also intends to develop rare earth metals, given their importance for electronics, laser technology, communication and medical equipment. The second five-year plan coincides with the development of the Business 2020 roadmap for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which makes provision for the allocation of grants to SMEs in the regions and for microcredit. The government and the National Chamber of Entrepreneurs also plan to develop an effective mechanism to help start-ups.[215]

During subsequent five-year plans to 2050, new industries will be established in fields such as mobile, multi-media, nano- and space technologies, robotics, genetic engineering and alternative energy. Food processing enterprises will be developed with an eye to turning the country into a major regional exporter of beef, dairy and other agricultural products. Low-return, water-intensive crop varieties will be replaced with vegetable, oil and fodder products. As part of the shift to a "green economy" by 2030, 15% of acreage will be cultivated with water-saving technologies. Experimental agrarian and innovational clusters will be established and drought-resistant genetically modified crops developed.[215]
The Kazakhstan 2050 Strategy fixes a target of devoting 3 percent of GDP to research and development by 2050 to allow for the development of new high-tech sectors.[215]
The Digital Kazakhstan program was launched in 2018 to boost the country's economic growth through the implementation of digital technologies. Kazakhstan's digitization efforts generated 800 billion tenges (US$1.97 billion) in two years. The program helped create 120,000 jobs and attracted 32.8 billion tenges (US$80.7 million) of investment into the country.
Around 82 percent of all public services became automated as part of the Digital Kazakhstan program.[217]
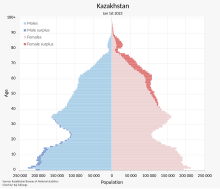

The US Census Bureau International Database lists the population of Kazakhstan as 18.9 million (May 2019),[218] while United Nations sources such as the 2022 revision of the World Population Prospects[219][220] give an estimate of 19,196,465. Official estimates put the population of Kazakhstan at 20 million as of November 2023.[221] In 2013, Kazakhstan's population rose to 17,280,000 with a 1.7 percent growth rate over the past year according to the Kazakhstan Statistics Agency.[222]
The 2009 population estimate is 6.8 percent higher than the population reported in the last census from January 1999. The decline in population that began after 1989 has been arrested and possibly reversed. Men and women make up 48.3 and 51.7 percent of the population, respectively.
As of 2024, ethnic Kazakhs are 71 percent of the population and ethnic Russians are 14.9 percent.[223] Other groups include Tatars (1.1 percent), Ukrainians (1.9 percent), Uzbeks (3.3 percent), Germans (1.1 percent), Uyghurs (1.5 percent), Azerbaijanis, Dungans, Turks, Koreans, Poles, and Lithuanians. Some minorities such as Ukrainians, Koreans, Volga Germans (0.9 percent), Chechens,[224] Meskhetian Turks, and Russian political opponents of the regime, had been deported to Kazakhstan in the 1930s and 1940s by Josef Stalin. Some of the largest Soviet labour camps (Gulag) existed in the country.[225]

Significant Russian immigration was also connected with the Virgin Lands Campaign and Soviet space program during the Khrushchev era.[226] In 1989, ethnic Russians were 37.8 percent of the population and Kazakhs held a majority in only 7 of the 20 regions of the country. Before 1991 there were about one million Germans in Kazakhstan, mostly descendants of the Volga Germans deported to Kazakhstan during World War II. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, most of them emigrated to Germany.[227] Most members of the smaller Pontian Greek minority have emigrated to Greece. In the late 1930s thousands of Koreans in the Soviet Union were deported to Central Asia.[228] These people are now known as Koryo-saram.[229]
The 1990s were marked by the emigration of many of the country's Russians, Ukrainians and Volga Germans, a process that began in the 1970s. This has made indigenous Kazakhs the largest ethnic group.[230] Additional factors in the increase in the Kazakhstani population are higher birthrates and immigration of ethnic Kazakhs from China, Mongolia, and Russia.
Kazakhstan is officially a bilingual country.[231] Kazakh (part of the Kipchak sub-branch of the Turkic languages)[232] is proficiently spoken by 80.1% of the population according to 2021 census,[233] and has the status of "state language". Russian, on the other hand, is spoken by 83.7% as of 2021.[234] It has equal status to Kazakh as an "official language", and is used routinely in business, government, and inter-ethnic communication.[235]
The government announced in January 2015 that the Latin alphabet will replace Cyrillic as the writing system for the Kazakh language by 2025.[236] Other minority languages spoken in Kazakhstan include Uzbek, Ukrainian, Uyghur, Kyrgyz, Tatar, and German. English, as well as Turkish, have gained popularity among younger people since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Education across Kazakhstan is conducted in either Kazakh, Russian, or both.[237] In Nazarbayev's resignation speech of 2019, he projected that the people of Kazakhstan in the future will speak three languages (Kazakh, Russian and English).[238]



According to the 2021 census, 69.3% of the population is Muslim, 17.2% are Christian, 0.2% follow other religions (mostly Buddhist and Jewish), 11.01% chose not to answer, and 2.25% identify as atheist.[3][4]
Kazakhstan is a secular state whose constitution guarantees religious freedoms. Article 39 of the constitution states: "Human rights and freedoms shall not be restricted in any way." Article 14 prohibits "discrimination on religious basis" and Article 19 ensures that everyone has the "right to determine and indicate or not to indicate his/her ethnic, party and religious affiliation." The Constitutional Council affirmed these rights in a 2009 declaration, which stated that a proposed law limiting the rights of certain individuals to practice their religion was declared unconstitutional.[239]
Islam is the largest religion in Kazakhstan, followed by Eastern Orthodox Christianity. After decades of religious suppression by the Soviet Union, the coming of independence witnessed a surge in the expression of ethnic identity, partly through religion. The free practice of religious beliefs and the establishment of full freedom of religion led to an increase of religious activity. Hundreds of mosques, churches, and other religious structures were built in the span of a few years, with the number of religious associations rising from 670 in 1990 to 4,170 today.[240]
Some figures show that non-denominational Muslims[241] form the majority, while others indicate that most Muslims in the country are Sunnis following the Hanafi school.[242] These include ethnic Kazakhs, who constitute about 70% of the population, as well as ethnic Uzbeks, Uighurs, and Tatars.[243] Less than 1% are part of the Sunni Shafi`i school (primarily Chechens). There are also some Ahmadi Muslims.[244] There are a total of 2,300 mosques,[240] all of them are affiliated with the "Spiritual Association of Muslims of Kazakhstan", headed by a supreme mufti.[245] Unaffiliated mosques are forcefully closed.[246] Eid al-Adha is recognised as a national holiday.[240] One quarter of the population is Russian Orthodox, including ethnic Russians, Ukrainians and Belarusians.[247] Other Christian groups include Roman Catholics, Greek Catholics, and Protestants.[243] There are a total of 258 Orthodox churches, 93 Catholic churches (9 Greek Catholic), and over 500 Protestant churches and prayer houses. The Russian Orthodox Christmas is recognised as a national holiday in Kazakhstan.[240] Other religious groups include Judaism, the Baháʼí Faith, Hinduism, Buddhism, and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.[243]
According to the 2009 Census data, there are very few Christians outside the Slavic and Germanic ethnic groups.[248]

Education is universal and mandatory through to the secondary level and the adult literacy rate is 99.5%.[249] On average, these statistics are equal to both women and men in Kazakhstan.[250]
Education consists of three main phases: primary education (forms 1–4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and vocational education. Vocational Education usually lasts three or four years.[251] (Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education.) These levels can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g., primary school, then secondary school). Recently, several secondary schools, specialised schools, magnet schools, gymnasiums, lyceums and linguistic and technical gymnasiums have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and vocational schools.[249]
At present, there are universities, academies and institutes, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. There are three main levels: basic higher education that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to the award of the Bachelor's degree; specialised higher education after which students are awarded the Specialist's Diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education which leads to the master's degree. Postgraduate education leads to the Kandidat Nauk ("Candidate of Sciences") and the Doctor of Sciences (PhD). With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed.
Over 2,500 students in Kazakhstan have applied for student loans totalling about $9 million. The largest number of student loans come from Almaty, Astana and Kyzylorda.[252]
The training and skills development programs in Kazakhstan are also supported by international organisations. For example, on 30 March 2015, the World Banks' Group of Executive Directors approved a $100 million loan for the Skills and Job project in Kazakhstan.[253] The project aims to provide training to unemployed, unproductively self-employed, and employees in need of training.[253]
Before the Russian colonisation, the Kazakhs had a highly developed culture based on their nomadic pastoral economy. Islam was introduced into the region with the arrival of the Arabs in the 8th century. It initially took hold in the southern parts of Turkestan and spread northward.[254] The Samanids helped the religion take root through zealous missionary work. The Golden Horde further propagated Islam amongst the tribes in the region during the 14th century.[255]
Kazakhstan is home to a large number of prominent contributors to literature, science and philosophy: Abay Qunanbayuli, Mukhtar Auezov, Gabit Musirepov, Kanysh Satpayev, Mukhtar Shakhanov, Saken Seyfullin, Jambyl Jabayev, among many others.
Tourism is a rapidly growing industry in Kazakhstan and it is joining the international tourism networking. In 2010, Kazakhstan joined The Region Initiative (TRI) which is a Tri-regional Umbrella of Tourism-related organisations. TRI is functioning as a link between three regions: South Asia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe. Armenia, Bangladesh, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, Russia, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Turkey, and Ukraine are now partners, and Kazakhstan is linked with other South Asian, Eastern European, and Central Asian countries in the tourism market.
Kazakh literature is defined as "the body of literature, both oral and written, produced in the Kazakh language by the Kazakh people of Central Asia".[256] Kazakh literature expands from the current territory of Kazakhstan, also including the era of Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, Kazakh recognised territory under the Russian Empire and the Kazakh Khanate. There is some overlap with several complementary themes, including the literature of Turkic tribes that inhabited Kazakhstan over the course of its history and literature written by ethnic Kazakhs.

According to Chinese written sources from the 6th–8th centuries CE, the Turkic tribes of Kazakhstan had an oral poetry tradition. These came from earlier periods and were primarily transmitted by bards: professional storytellers and musical performers.[257] Traces of this tradition are shown on Orkhon script stone carvings dated 5th–7th centuries CE that describe rule of Kultegin and Bilge, two early Turkic rulers ("kagans").[citation needed] Amongst the Kazakhs, the bard was a primarily, though not exclusively, male profession. Since at least the 17th century, Kazakh bards could be divided into two main categories: the zhıraws (zhiraus, žyraus), who passed on the works of others, usually not creating and adding their own original work; and the aqyns (akyns), who improvised or created their own poems, stories or songs.[256] There were several types of works, such as didactic termes, elegiac tolgaws, and epic zhırs.[256] Although the origins of such tales are often unknown, most of them were associated with bards of the recent or more distant past, who supposedly created them or passed them on, by the time most Kazakh poetry and prose was first written down in the second half of the 19th century.[256] There are clear stylistic differences between works first created in the 19th century, and works dating from earlier periods but not documented before the 19th century, such as those attributed to such 16th- and 17th-century bards as Er Shoban and Dosmombet Zhıraw (also known as Dospambet Žyrau; he appeared to have been literate, and reportedly visited Constantinople), and even to such 15th-century bards as Shalkiz and Asan Qayghı.[256]
Other notable bards include Kaztugan Žyrau, Žiembet Žyrau, Axtamberdy Žyrau, and Buxar Žyrau Kalkamanuly, who was an advisor to Ablai Khan, and whose works have been preserved by Mäšhür Žüsip Köpeev.[257] Er Targhın and Alpamıs are two of the most famous examples of Kazakh literature to be recorded in the 19th century.[256] The Book of Dede Korkut and Oguz Name (a story of an ancient Turkic king Oghuz Khan) are the most well-known Turkic heroic legends. Initially created around the 9th century CE, they were passed on through generations in oral form. The legendary tales were recorded by Turkish authors in 14–16th centuries C.E.[258][259]
The preeminent role in the development of modern literary Kazakh belongs to Abai Qunanbaiuly (Kazakh: Абай Құнанбайұлы, sometimes Russified to Abay Kunanbayev, Абай Кунанбаев) (1845–1904), whose writings did much to preserve Kazakh folk culture. Abai's major work is The Book of Words (Kazakh: қара сөздері, Qara sözderi), a philosophical treatise and collection of poems where he criticises Russian colonial policies and encourages other Kazakhs to embrace education and literacy. The literary magazines Ay Qap (published between 1911 and 1915 in Arabic script) and Qazaq (published between 1913 and 1918) played an important role in the development of the intellectual and political life among early 20th-century Kazakhs.[260]

The modern state of Kazakhstan is home to the Kazakh State Kurmangazy Orchestra of Folk Instruments, the Kazakh State Philharmonic Orchestra, the Kazakh National Opera and the Kazakh State Chamber Orchestra. The folk instrument orchestra was named after Kurmangazy Sagyrbayuly, a famous composer and dombra player from the 19th century. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1931, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed.[261]The Foundation Asyl Mura is archiving and publishing historical recordings of great samples of Kazakh music both traditional and classical. The leading conservatoire is in Almaty, the Qurmanghazy Conservatoire. It competes with the national conservatoire in Astana, Kazakhstan's capital.
When referring to traditional Kazakh music, authentic folklore must be separated from "folklorism". The latter denotes music executed by academically trained performers who aim at preserving the traditional music for coming generations. As far as can be reconstructed, the music of Kazakhstan from the period before a strong Russian influence consists of instrumental music and vocal music. Instrumental music, with the pieces ("Küy") being performed by soloists. Text is often seen in the background (or "program") for the music, as a lot of Küy titles refer to stories. Vocal music, either as part of a ceremony such as a wedding (mainly performed by women), or as part of a feast. Here we might divide into subgenres: epic singing, containing not only historical facts, but as well the tribe's genealogy, love songs, and didactic verses; and as a special form the composition of two or more singers in public (Aitys), of dialogue character and usually unexpectedly frankly in content.

The Russian influence on the music life in Kazakhstan can be seen in two spheres: first, the introduction of musical academic institutions such as concert houses with opera stages, and conservatories, where European music was performed and taught, and second, by trying to incorporate Kazakh traditional music into these academic structures. Controlled first by the Russian Empire and then the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan's folk and classical traditions became connected with ethnic Russian music and Western European music. Prior to the 20th century, Kazakh folk music was collected and studied by ethnographic research teams including composers, music critics and musicologists. In the first part of the 19th century, Kazakh music was transcribed in linear notation. Some composers of this era set Kazakh folk songs to Russian-style European classical music.
The Kazakhs themselves, however, did not write their own music in notation until 1931. Later, as part of the Soviet Union, Kazakh folk culture was encouraged in a sanitised manner designed to avoid political and social unrest. The result was a bland derivative of real Kazakh folk music. In 1920, Aleksandr Zatayevich, a Russian official, created major works of art music with melodies and other elements of Kazakh folk music. Beginning in 1928 and accelerating in the 1930s, he also adapted traditional Kazakh instruments for use in Russian-style ensembles, such as by increasing the number of frets and strings. Soon, these styles of modern orchestral playing became the only way for musicians to officially play; Kazakh folk was turned into patriotic, professional and socialist endeavours.[262]
In Kazakhstan, the fine arts, in the classical sense, have their origins in the second half of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century. It was largely influenced by Russian artists, such as Vasily Vereshchagin and Nikolai Khludov, who intensively travelled in Central Asia. Khludov had a particular influence on the development of the local school of painting, becoming the teacher of many local artists. The most famous of these is Abilkhan Kasteyev, after whom the State Museum of Art of Kazakhstan was renamed in 1984.[263]
The Kazakh school of fine arts was fully formed by the 1940s and flourished in the 1950s. Local painters, graphic artists and sculptors, trained under the unified Soviet system of artist education, began active work, often using national motifs in their art. The painters O. Tansykbaev, J. Shardenov, K. Telzhanov, and S. Aitbaev, graphic artists E. Sidorkina and A. Duzelkhanov, and sculptors H. Nauryzbaeva and E. Sergebaeva are today counted among the key figures of Kazakhstani art.
In the national cuisine, livestock meat, like horse meat[264] and beef can be cooked in a variety of ways and is usually served with a wide assortment of traditional bread products. Refreshments include black tea, often served with milk and dried fruits (such as dried apricots) and nuts. In southern provinces, people often prefer green tea. Traditional milk-derived drinks such as ayran, shubat and kymyz. A traditional Kazakh dinner involves a multitude of appetisers on the table, followed by a soup and one or two main courses such as pilaf and beshbarmak. They also drink their national beverage, kumys, which consists of fermented mare's milk.[265]

Kazakhstan consistently performs in Olympic competitions. It is especially successful in boxing. This has brought some attention to the Central Asian nation and increased world awareness of its athletes. Dmitry Karpov and Olga Rypakova are among the most notable Kazakhstani athletes. Dmitry Karpov is a distinguished decathlete, taking bronze in both the 2004 Summer Olympics, and the 2003 and 2007 World Athletics Championships. Olga Rypakova is an athlete, specialising in triple jump (women's), taking silver in the 2011 World Championships in Athletics and Gold in the 2012 Summer Olympics. Kazakhstan's city of Almaty submitted bids twice for the Winter Olympics: in 2014 and again for the 2022 Winter Olympics. Astana and Almaty hosted the 2011 Asian Winter Games.[266]
Popular sports in Kazakhstan include football, basketball, ice hockey, bandy, and boxing.
Football is the most popular sport in Kazakhstan. The Football Federation of Kazakhstan is the sport's national governing body. The FFK organises the men's, women's, and futsal national teams.
Kazakhstan's most famous basketball player was Alzhan Zharmukhamedov, who played for CSKA Moscow and the Soviet Union's national basketball team in the 1960s and 1970s. Kazakhstan's national basketball team was established in 1992, after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Since its foundation, it has been competitive at the continental level. Its greatest accomplishment was at the 2002 Asian Games, where it defeated the Philippines in its last game to win the bronze medal. At the official Asian Basketball Championship, now called FIBA Asia Cup, the Kazakhs' best finish was 4th place in 2007.
The Kazakhstan national bandy team is among the best in the world, and has many times won the bronze medal at the Bandy World Championship, including the 2012 edition when Kazakhstan hosted the tournament on home ice.[267][268] The team won the first bandy tournament at the Asian Winter Games. During the Soviet time, Dynamo Alma-Ata won the Soviet Union national championships in 1977 and 1990 and the European Cup in 1978. Bandy is developed in ten of the country's seventeen administrative divisions (eight of the fourteen regions and two of the three cities which are situated inside of but are not part of regions).[269] Akzhaiyk from Oral, however, is the only professional club.

The Kazakh national ice hockey team have competed in ice hockey in the 1998 and 2006 Winter Olympics, as well as in the 2006 Men's World Ice Hockey Championships. The Kazakhstan Hockey Championship is held since 1992. Barys Astana is the main domestic Kazakhstani ice hockey professional team, and having played in the Kazakhstani national league until the 2008–09 season, when they were transferred to play in the Kontinental Hockey League. Meanwhile, the Kazzinc-Torpedo and play in the Supreme Hockey League since 1996 and the Saryarka Karagandy since 2012. Top Kazakhstani ice hockey players include Nik Antropov, Ivan Kulshov and Evgeni Nabokov.
Kazakh boxers are generally well known in the world. In the last three Olympic Games, their performance was assessed as one of the best and they had more medals than any country in the world, except Cuba and Russia (in all three games). In 1996 and 2004, three Kazakhstani boxers (Vassiliy Jirov in 1996, Bakhtiyar Artayev in 2004 and Serik Sapiyev in 2012) were recognised as the best boxers for their techniques with the Val Barker Trophy, awarded to the best boxer of the tournament. In boxing, Kazakhstan performed well in the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney. Two boxers, Bekzat Sattarkhanov and Yermakhan Ibraimov, earned gold medals. Another two boxers, Bulat Zhumadilov and Mukhtarkhan Dildabekov, earned silver medals. Oleg Maskaev, born in Zhambyl, representing Russia, was the WBC Heavyweight Champion after knocking out Hasim Rahman on 12 August 2006. The reigning WBA, WBC, IBF and IBO middleweight champion is Kazakh boxer Gennady Golovkin. Natascha Ragosina, representing Russia, but from Qarağandy held seven versions of the women's super middleweight title, and two heavyweight titles during her boxing career. She holds the record as the longest-reigning WBA female super middleweight champion, and the longest-reigning WBC female super middleweight champion.

Kazakhstan's film industry is run through the state-owned Kazakhfilm studios based in Almaty. The studio has produced movies such as Myn Bala, Harmony Lessons, and Shal.[270] Kazakhstan is the host of the International Astana Action Film Festival and the Eurasia International Film Festival held annually. Hollywood director Timur Bekmambetov is from Kazakhstan and has become active in bridging Hollywood to the Kazakhstan film industry.[271]
Kazakhstan journalist Artur Platonov won Best Script for his documentary "Sold Souls" about Kazakhstan's contribution to the struggle against terrorism at the 2013 Cannes Corporate Media and TV Awards.[272][273]
Serik Aprymov's Little Brother (Bauyr) won at the Central and Eastern Europe Film Festival goEast from the German Federal Foreign Office.[274]

Kazakhstan is ranked 161 out of 180 countries on the Reporters Without Borders World Press Freedom Index[275] A mid-March 2002 court order, with the government as a plaintiff, stated that Respublika were to stop printing for three months.[276] The order was evaded by printing under other titles, such as Not That Respublika.[276] In early 2014, a court also issued a cease publication order to the small-circulation Assandi-Times newspaper, saying it was a part of the Respublika group. Human Rights Watch said: "this absurd case displays the lengths to which Kazakh authorities are willing to go to bully critical media into silence."[277]
With support from the US Department of State's Bureau for Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (DRL), the American Bar Association Rule of Law Initiative opened a media support centre in Almaty to assist press outlets in Kazakhstan.[278]

Kazakhstan has three cultural and two natural sites on the UNESCO World Heritage list. The cultural sites are:
The natural sites are:
The wide distribution of the Turkic languages from Northwest China, Mongolia and Siberia in the east to Turkey and Bulgaria in the west implies large-scale migrations out of the homeland in Mongolia.The quotation is from pp. 4–5.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)For its part, the Assembly might decide, already at this stage, to interpret Rule 59 of its Rules of procedure, concerning special guests, in such a way as to include the Eurasian States. Two Council of Europe member States, Turkey and Russia, belong geographically to both Europe and Asia and are therefore Eurasian. Strictly speaking, the three South Caucasus States, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia are located in Asia, yet their membership of political Europe is no longer in doubt. [...] This being the case, Kazakhstan, as a Eurasian State participating in the OSCE and a signatory to the International covenant on civil and political rights and the International covenant on economic, social and cultural rights, would meet the criteria laid down in Rule 59, making it eligible to apply for special guest status with the Assembly.
However, by 2006, a Rapporteur for the Political Affairs Committee concluded that because of Kazakhstan's nature as a European country, the country should be considered 'eligible to apply for a special guest status.'
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link){{cite book}}: |website= ignored (help)![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from UNESCO Science Report: towards 2030, 365–387, UNESCO, UNESCO Publishing.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0. Text taken from UNESCO Science Report: towards 2030, 365–387, UNESCO, UNESCO Publishing.
General
Government
Trade
48°N 68°E / 48°N 68°E / 48; 68